
A Guide to Web3 Authentication
Written by Alchemy Team

Web3 authentication verifies users through their public keys rather than traditional emails or passwords. While this cryptographic approach eliminates centralized password databases and gives users true ownership of their digital credentials, the complexity of seed phrases, hexadecimal addresses, and key management has created significant barriers to mainstream adoption. Recent innovations in embedded wallets, account abstraction, and smart contract accounts are solving these challenges.
This guide explains how web3 authentication works, explores the technical solutions making it more accessible, and shows you how to implement production-ready authentication using modern smart wallet infrastructure.
How Does Web3 Authentication Work?
Traditional web authentication relies on credentials stored on centralized servers. You enter a username and password, the server checks its database, and grants access if the credentials match. This model requires users to trust the service provider with their authentication data.
Web3 authentication flips this model. Users authenticate by connecting web3 wallets to applications, typically by signing a transaction. Here's the technical flow:
1. Wallet Connection
When a user clicks "Connect Wallet," the app initiates a connection request to the user's wallet software (like MetaMask, Phantom, or Rainbow). This connection doesn't grant any permissions yet. It simply establishes a communication channel.
2. Challenge Generation
The app generates a unique challenge message. This is typically a random nonce or a formatted message that includes the app domain, timestamp, and purpose of the authentication request. This prevents replay attacks.
3. Cryptographic Signing
The user's wallet signs the challenge message using their private key. A private key, which is kept secret, is used to prove ownership of a corresponding public key. The signature proves that the user controls the private key associated with their wallet address without revealing the key itself.
4. Signature Verification
The app verifies the signature using the user's public key (wallet address). If the signature is valid, the app confirms the user owns that wallet address and grants access. This verification happens client-side or on your backend, depending on your architecture.
5. Session Management
Once authenticated, the app typically issues a session token for subsequent requests, similar to traditional web sessions. This prevents users from signing messages for every action.
The cryptographic foundation makes this process more secure than password-based authentication in several ways. There's no password to steal from a database breach. Phishing attacks require tricking users into signing malicious transactions, which is more visible than stealing a password. Users maintain control over their authentication credentials rather than trusting a centralized provider.
What Are the Current Problems with Web3 Authentication?
Despite its cryptographic advantages, web3 authentication presents significant user experience challenges that limit mainstream adoption. Understanding these problems is essential for building solutions that work for broader audiences.
How Do Seed Phrases Impact User Experience?
Web3 requires users to set up a wallet, manage private keys, store seed phrases, and often work with messy browser extensions or mobile apps. The seed phrase model, where users must write down and securely store 12-24 random words, is fundamentally incompatible with mainstream user expectations.
Data shows that 35% of users never back up their wallet seed phrases, putting them at serious risk of losing access to their funds. This isn't user error, it's a design problem. For years, we've been able to reset passwords through email recovery. With cryptocurrency wallets, seed phrases work differently: if you lose them, there's no reset option. This is a key difference that's worth understanding before getting started.
Why Is Wallet UX Confusing?
Signing in crypto feels like reading a user license agreement, except instead of legal jargon, you get hex code and raw function calls. When users click "Sign" in their wallet, they're often presented with:
Raw transaction data in hexadecimal format
Gas fee estimates in Gwei
Contract addresses they don't recognize
Function calls like
approve(address,uint256)
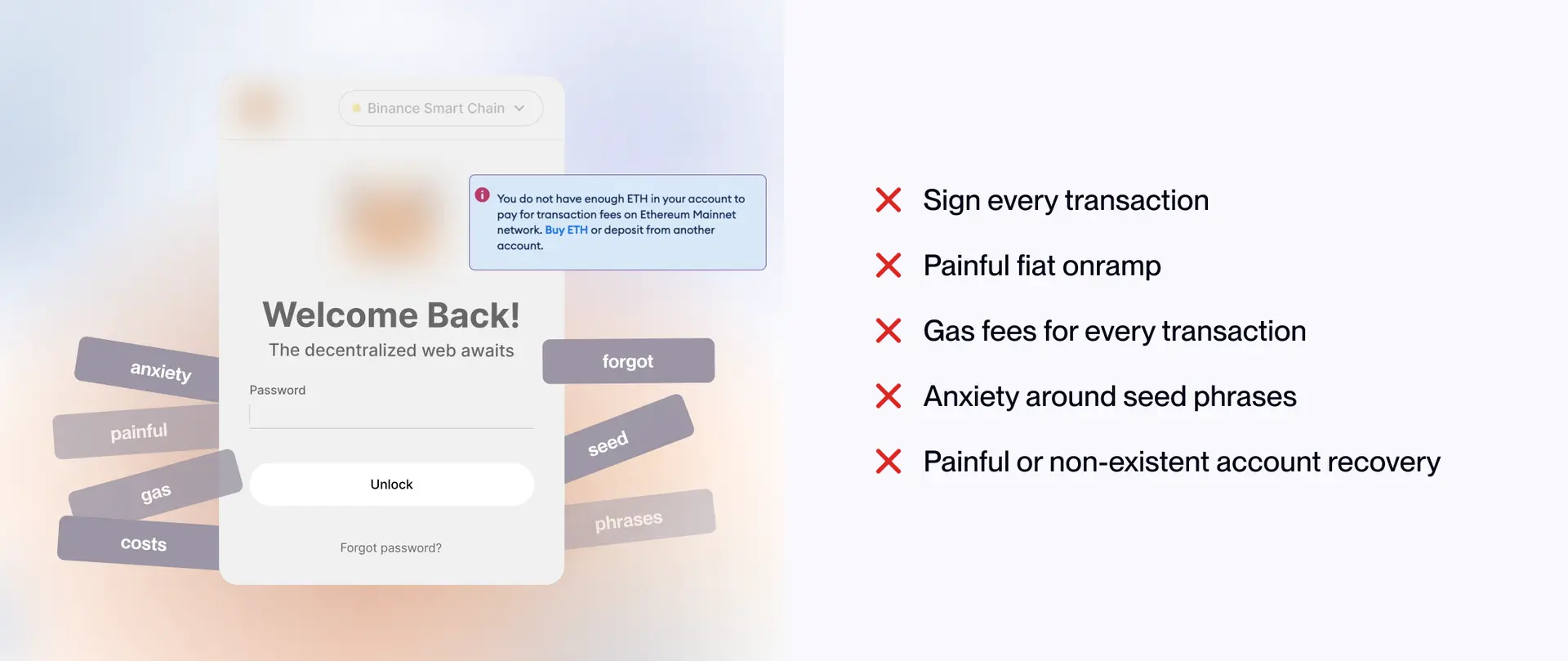
Users lack the context to evaluate whether these transactions are legitimate or malicious. This information asymmetry creates security vulnerabilities. Users click "Confirm" without understanding what they're authorizing.
What Technical Barriers Do Users Face?
Users are faced with multiple blockchain networks, hexadecimal addresses, and gas fees before they can even attempt to log in. Consider the cognitive load:
Network selection: Should they use Ethereum mainnet, Polygon, Arbitrum, Base, or Optimism?
Address management: Understanding that
0x742d35Cc6634C0532925a3b844Bc9e7595f0bEbrepresents their accountGas fees: Needing to hold native tokens (ETH, MATIC, etc.) just to authenticate
Browser extensions: Installing and managing separate wallet software
Each of these represents a point of friction where users drop off.
How Does Wallet Fragmentation Affect Users?
Many Web3 users manage multiple wallets with separate keys and recovery phrases, each requiring protection. A user might have:
One wallet for Ethereum and EVM chains
A separate Solana wallet
Different wallets for different apps or use cases
Hardware wallets for high-value assets
Managing this fragmentation requires technical knowledge and organizational discipline that most users don't have.
What Security Risks Does Current Authentication Create?
Smart contracts and DeFi platforms are frequently targeted by hackers, with phishing attacks tricking users into revealing their private keys. The authentication mechanism itself becomes the attack surface when:
Approval phishing: Users unknowingly sign unlimited token approvals
Domain spoofing: Fake sites that mimic legitimate apps
Social engineering: Attackers impersonate support to obtain seed phrases
Malicious contracts: Users interact with contracts that drain their wallets
The security of private keys is paramount in Web3, since losing access to a private key can mean losing access to your digital identity and assets. This creates a high-stakes environment where a single mistake can be catastrophic.
How Is Web3 Authentication Improving?
The onchain ecosystem is actively addressing these challenges through several technical innovations that dramatically improve authentication UX without sacrificing security or decentralization.
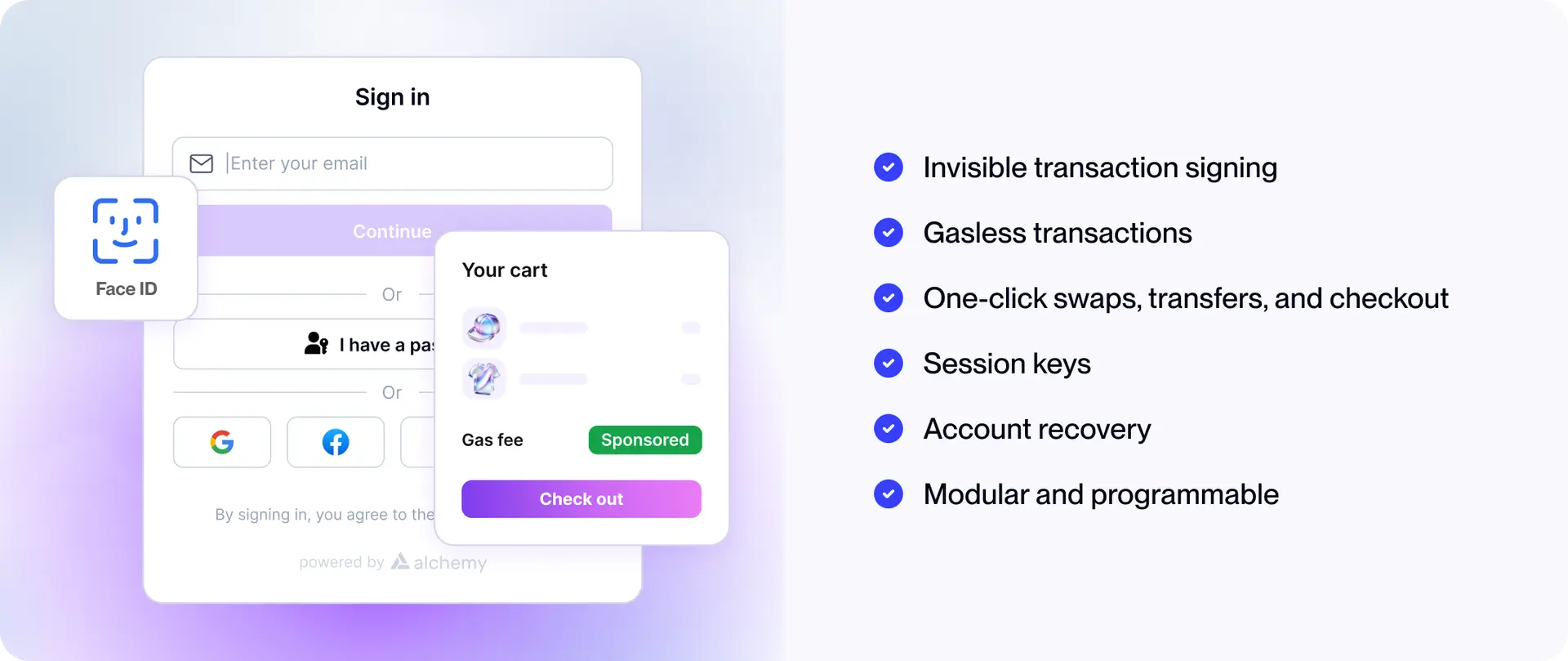
What Are Embedded Wallets?
Embedded wallets are built directly into Web3 applications, have a familiar login experience, and don't require a seed phrase to be memorized and kept. Instead of requiring users to install a browser extension or separate wallet app, the wallet functionality is integrated directly into your application.
With embedded wallets, a user can choose to log in with their Google, Apple ID, or X account, and behind the scenes, a self-custodial wallet is created on their behalf. This approach provides several key benefits:
Familiar Authentication Flows
Users authenticate using methods they already understand: email, OAuth, or biometrics. Wallet creation and recovery are handled using familiar authentication flows, eliminating the need for users to understand or manage private keys directly.
No Browser Extensions
The wallet exists within your app's context. Users don't need to install MetaMask or any other third-party software. This removes a major onboarding barrier and gives you complete control over the authentication experience.
Seamless UX
Because the wallet is embedded into your app's UI, you maintain full control over the look, feel, and flow, with no pop-ups or redirect screens. The authentication happens inline with your existing user experience.
How Do Social Logins Enable Web3 Access?
Social login integration bridges the gap between Web2 and Web3 by leveraging existing authentication providers. Here's how the technical architecture works:
Key Splitting via MPC
TSS-MPC, or Threshold Signature Scheme with Multi-Party Computation, is a cryptographic method that allows multiple parties to jointly generate a single digital signature, enhancing security by distributing the signing power among participants without revealing the private key to any single party.
When a user signs in with Google:
Your app authenticates the user via OAuth
The system generates a private key split across multiple parties
No single party (including your application) has access to the full key
Transaction signing requires threshold cooperation between parties
The user maintains self-custody without managing keys directly
Passkey Authentication
Passkeys are a type of passwordless authentication designed to be more secure and convenient than traditional passwords, based on the WebAuthn standard. Passkeys use public key cryptography where:
The private key is stored in the user's device secure enclave (like Apple's Secure Enclave or Android's Trusted Execution Environment)
The public key is stored on your authentication server
Unlike traditional passwords, which create friction and pose phishing risks, passkeys leverage a familiar pattern of using a biometric to securely create and store a credential to the user's device.
This provides strong security (private keys never leave the device) with familiar UX (FaceID or TouchID).
What Is Account Abstraction and Why Does It Matter?
Account abstraction (ERC-4337) represents a fundamental shift in how onchain accounts work. Smart contract wallets that use Account Abstraction create a wallet that is managed using a smart contract instead of a wallet that is managed by a single private key.
Traditional Ethereum accounts (Externally Owned Accounts or EOAs) are controlled by a single private key. Smart contract accounts are controlled by code, which enables significantly more functionality:
Gas Sponsorship
With account abstraction, a user’s wallet or account becomes programmable, enabling developers to sponsor gas fees on behalf of the user. This means:
Users don't need to hold ETH to interact with your app
You can sponsor onboarding transactions to reduce friction
Users can pay gas fees in stablecoins or other ERC-20 tokens
You can set specific policies for which transactions to sponsor
Batched Transactions
As programmable smart accounts, transactions can be batched, simplifying UX enormously and cutting latency. Users can:
Approve a token and swap it in a single transaction
Mint an NFT and list it for sale atomically
Execute multi-step DeFi strategies without multiple wallet confirmations
Social Recovery
Smart contract accounts can implement recovery mechanisms that don't depend on seed phrases:
Designate trusted contacts who can help recover your account
Use email or phone-based recovery flows
Implement time-locked account recovery processes
Programmable Security
Because the account is a smart contract, you can implement custom logic:
Multi-signature requirements for high-value transactions
Spending limits per day or per transaction
Whitelisted addresses for automatic approval
Time-based restrictions on certain operations
Vitalik, the co-founder of Ethereum, sees a transition from EOAs to Smart Wallets as a requirement for getting mainstream users onchain. Account abstraction isn't a nice-to-have feature—it's foundational infrastructure for mainstream adoption.
How Do Passkeys Improve Authentication Security?
Passkeys come with multiple built-in security benefits. Specifically, unlike a password or passcode, a user doesn't have to remember information with a passkey, and that information can't be phished from the user.
The security model works as follows:
Device-Bound Credentials
The private key is generated and stored in the device's secure hardware (Trusted Platform Module, Secure Enclave, etc.). It never leaves the device, eliminating the risk of key theft through network attacks.
Phishing Resistance
Because passkeys are bound to the domain that created them, they can't be used on phishing sites. Even if a user is tricked into visiting a fake site, the passkey won't work because the domain doesn't match.
No Shared Secrets
Unlike passwords, which are shared secrets between user and server, passkeys use asymmetric cryptography. The server only stores the public key, which is useless to attackers even if the database is breached.
Biometric Authentication
In addition, because passkeys are tied to your iCloud or Google accounts, they are protected by Apple and Google's security. This provides:
Multi-factor authentication by default (possession of device + biometric)
Protection against SIM swapping attacks
Backup and sync across devices
What Developer Solutions Make Web3 Auth Easy?
Several providers offer infrastructure to simplify web3 authentication implementation. Here's what you need to know about the landscape.
What Third-Party Authentication Providers Are Available?
Web3Auth
A simple, non-custodial auth infrastructure that enables Web3 wallets and applications to provide seamless user logins to both mainstream and native Web3 users. Web3Auth supports social logins, email authentication, and integrates with multiple wallet providers.
Magic
Offers email-based wallet creation with multi-party computation for key management. Magic handles the complexity of key splitting and recovery while providing a simple API for developers.
Dynamic
Provides non-custodial embedded wallets with support for social login and account abstraction integrations. Dynamic offers both embedded wallets and support for external wallet connections.
Privy
Powers hardware-secured, SOC 2-compliant wallets for any user across EVM, Solana, Bitcoin, and more. Privy focuses on seamless login with enterprise-grade security with passkey and hardware token support.
How Does Alchemy's Smart Wallet Infrastructure Work?
We built Smart Wallets to provide vertically integrated wallet and transaction infrastructure. Instead of stitching together multiple services, you get everything you need to implement production-ready authentication in a single SDK.
Embedded Wallets for Zero-Friction Onboarding
Smart Wallets makes it possible to build products that feel like web2 but are fully web3 under the hood. Here's what this means in practice:
Users can sign up using:
Email authentication
Social logins (Google, Apple, Twitter)
Passkeys (FaceID, TouchID)
Custom authentication (bring your own authentication method)
Traditional wallet connections for crypto-native users
The implementation is straightforward. Here's a guide that will help you get started.
Smart Contract Account Creation
Once authenticated, you create a smart contract account for the user. All our smart contract accounts are audited by Quantstamp and battle-tested in production with over 380M+ transactions:
The smart contract account provides all the benefits of account abstraction—gas sponsorship, batched transactions, and programmable security.
Gas Sponsorship Configuration
Sponsor gas through programmable policies. You control exactly which transactions to sponsor and do it with any ERC-20.
Set policies via our dashboard:
Spending limits per wallet or globally
Allowlist/blocklist specific addresses
Sponsor specific contract interactions
Set daily/monthly spending caps
Multi-Chain Support
Smart Wallets are available on 30+ chains including Ethereum, Polygon, Base, Optimism, Arbitrum, and more. Write your authentication logic once and deploy across multiple chains.
Production-Ready Infrastructure
Built on Alchemy's best-in-class, reliable infrastructure, so smart contract wallet primitives are always available to users. We provide:
99.99% uptime SLA
Sub-second response times
Automatic scaling
24/7 support for enterprise customers
Alchemy Smart Wallets have powered over 380B+ transactions are the #1 most used smart wallet, powering applications from small startups to large enterprises.
How Should You Implement Web3 Authentication?
Based on building authentication for thousands of apps, here are the patterns that work in production.
Should You Start with Social Login or Wallet Connect?
For apps targeting mainstream users, start with social login. For apps targeting crypto-native users, support both.
Social Login First Pattern: This approach maximizes conversion for new users who don't own crypto wallets. You can always add an "export to MetaMask" feature later for users who want full wallet control.
Wallet Connect First Pattern: This works well for DeFi apps, NFT marketplaces, or other apps where users likely already have wallets.
How Should You Handle Gas Fees?
Don't make users buy ETH before they can use your app. Sponsor gas so users can try your app for free, no ETH required. Configure sponsorship policies based on your business model:
Freemium Model:
Sponsor first N transactions per user
Require payment or staking after free tier
Monitor spend per wallet to prevent abuse
Subscription Model:
Sponsor all gas for paying subscribers
Limit sponsorship for free tier users
Transaction-Based Model:
Take a fee on each transaction
Sponsor gas as part of the transaction cost
Set global spending limits to control costs while providing smooth UX.
Should You Use Transaction Batching?
Yes, whenever users need multiple operations to complete a flow. The transactions are executed sequentially as they appear in the array, allowing you to:
Improve UX:
One confirmation instead of multiple wallet popups
Atomic execution (all operations succeed or all fail)
Lower total gas costs
Common Patterns:
Approve + Swap: Let users approve and execute swaps in one click
Mint + List: Create and list NFTs atomically
Multi-token operations: Interact with multiple contracts in one transaction
How Should You Handle Mobile Users?
Dynamic spent time optimizing to mobile flows, leveraging passkeys for easy FaceID and TouchID login and wallet creation. Mobile-first authentication is critical because:
Most users access apps from mobile devices
Biometric authentication is more accessible on mobile
Mobile wallet apps (MetaMask Mobile, Rainbow) require deep linking
Mobile Best Practices:
Prioritize passkeys: FaceID and TouchID provide the best mobile UX
Support WalletConnect: For users with mobile wallet apps
Test deep linking: Ensure smooth handoffs to wallet apps
Design for small screens: Authentication UI should work on 320px viewports
Minimize redirects: Keep users in your app context when possible
What About Progressive Disclosure?
Don't overwhelm new users with advanced features. Design your own checkout flow and sign transactions in the background initially, then gradually expose more control.
Phase 1: Invisible Wallet
Social login only
All transactions auto-signed
No wallet terminology visible
Gas sponsored completely
Phase 2: Basic Control
Show transaction confirmations
Let users view their wallet address
Display transaction history
Explain gas sponsorship
Phase 3: Advanced Features
Allow exporting to external wallets
Show advanced transaction details
Enable manual gas payment
Support hardware wallet signing
This approach maximizes conversion while still providing power users with control.
What Does the Future of Web3 Authentication Look Like?
The trajectory for onchain authentication is clear: invisible by default, powerful when needed.
Will Smart Accounts Replace EOAs?
Vitalik, the co-founder of Ethereum, sees a transition from EOAs to Smart Wallets as a requirement for getting mainstream users onchain. This isn't speculation—it's the technical roadmap.
Smart wallets provide:
Better security through programmable permissions
Superior UX through gas abstraction and batching
Account recovery without seed phrases
Cross-chain interoperability
The ecosystem is moving toward smart wallets as the default. EOAs will remain supported for backward compatibility, but new apps should build on smart wallet infrastructure.
How Will Chain Abstraction Impact Authentication?
Chain abstraction solves problems by letting users sign up in one go, with no keys, recovery phrases, or multiple wallets. Users shouldn't need to know which chain they're using.
Future authentication will:
Use the same account address across all chains
Abstract away chain-specific details
Route transactions to optimal chains automatically
Handle cross-chain operations transparently
This requires coordination between wallet providers, bridges, and applications, but the technical foundations are being built now.
Will Biometric Authentication Become Standard?
Users can generate a self-custodial wallet via biometrics with Face ID or Touch ID. Passkeys are already supported by Apple, Google, and Microsoft, with adoption accelerating.
Within 2-3 years, expect:
Passkeys as the default authentication method
Seed phrases only for advanced users who request them
Biometric authentication across all devices
Seamless sync via iCloud/Google accounts
What Role Will AI Play?
AI agents can turn chaotic DeFi spaghetti into seamless, human-friendly finance, and they can make crypto usable, not just technically possible. AI will impact authentication through:
Transaction Intent Parsing:
Users describe what they want to do in natural language
AI generates the appropriate transactions
Users approve with simple confirmations
Fraud Detection:
AI analyzes transaction patterns for anomalies
Warns users before they approve suspicious transactions
Learns from previous attacks to prevent new ones
Personalized Security:
Adaptive authentication based on risk levels
AI-recommended security settings
Automated security monitoring
How Can You Start Building Today?
The gap between web3's promise and its user experience is closing rapidly. Modern authentication infrastructure makes it possible to onboard mainstream users without sacrificing decentralization or security.
We built Smart Wallets to make this accessible to every developer. You get:
Embedded wallets with social login and passkeys
Smart accounts with gas sponsorship and batching
Enterprise-grade infrastructure with 99.99% uptime
Multi-chain support across EVM and Solana
Thousands of builders use our infrastructure to onboard millions of users. The future of authentication isn't about teaching users how blockchains work. It's about building systems so intuitive that users don't need to think about the underlying technology.
Ready to implement modern web3 authentication? Sign up for a developer account, get started with the docs and demo, and contact us for more information or integration help.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the basic steps to add wallet-based authentication to my app?
Integrate a wallet connection flow, have the user sign a unique message, verify that signature on your backend, then create a session token so the user stays logged in without re-signing every request.
How does signing a message prove a user owns a wallet?
The app sends a challenge message that only the holder of the wallet's private key can sign; the app then verifies the signature with the wallet's public address to confirm the user controls that address.
Should I use social login, wallet login, or both for web3 authentication?
For mainstream audiences, start with social login and optionally create a wallet behind the scenes, while crypto-native apps often prioritize direct wallet connection and may add social login as a fallback.
How do I manage sessions after a user authenticates with a wallet?
After verifying the signed message, issue a session token or cookie for subsequent API requests, similar to traditional web sessions, so users don't need to sign every action.
What are embedded wallets and how do they improve authentication?
Embedded wallets are built directly into applications, allowing users to authenticate with familiar methods like Google or Apple ID while a self-custodial wallet is created behind the scenes. This eliminates the need for browser extensions or seed phrase management.
How do passkeys make web3 authentication more secure?
Passkeys use device-bound credentials stored in secure hardware that never leave the device, are resistant to phishing attacks, and provide biometric authentication without sharing secrets with servers.
What is account abstraction and why does it matter for authentication?
Account abstraction enables smart contract accounts that can sponsor gas fees, batch transactions, and implement programmable security features like social recovery, eliminating many barriers that prevent mainstream adoption.
Should I sponsor gas fees for user authentication?
Yes, sponsoring gas fees removes a major barrier for new users who don't own crypto, allowing them to try your app without needing to buy ETH first.

Related overviews
ERC-4337 enables smart contract wallets on Ethereum without requiring any consensus-layer protocol changes.
Build wallet infrastructure that hides blockchain complexity. No seed phrases, no gas fees, just easy login.
Deep dive into MPC wallets and modern crypto security through distributed private key technology.