
Account Abstraction (ERC-4337) vs. Meta Transactions (ERC-2771)
Written by Harpalsinh Jadeja
Meta Transactions and Account Abstraction are techniques for improving the user experience of Ethereum. Meta Transactions require a smart contract update, which is why they're being phased out.
How is Account Abstraction different from Meta Transactions?
Account Abstraction aims to abstract away more complexities of the Ethereum Account than just gas fees.
From a technical perspective, the difference between meta transactions and Account Abstraction lies in the structure of the message and its backwards compatibility.
Learn More About Account Abstraction
What are UserOps in Account Abstraction?
In the case of Meta Transactions, the industry standard was to use EIP712-based messages, which required all smart contracts to be upgraded.
Account Abstraction standardizes a special transaction format called UserOperations.
UserOperation contains all the information needed to figure out what transaction the user intends to perform, including fields to decide which Paymaster to use, how much the user is willing to pay (in case of self-sponsorship), and the signed UserOperation.
What are Paymasters in Account Abstraction?
The Gas abstraction portion of the ERC-4337 Account Abstraction standard introduces Paymasters.
Paymasters are onchain smart contracts that have arbitrary validation logic which can be used to define a valid gas sponsorship. Again, the difference here is the execution is onchain.
DAOs, dapps, and other teams can deploy their own custom paymasters with features such as ERC-20 gas payments and more.
These custom Paymasters can use ERC-4337 to plug and play with existing Bundler Services. This is different from Meta Transactions which require Provider adoption.
Sponsor transactions with our Gas Manager API
Relayers vs. Paymasters
While Relayers in the Meta Transaction concept are private keys under the control of Infra providers, Account Abstraction Bundlers are standardized nodes. Switching between different Bundlers is as simple as changing API keys and API URLs.
There is no concept of MinimalForwarder in Account Abstraction as sponsorship validation is done onchain inside the Paymaster contract.
Instead of having only one transaction inside a native transaction in the case of Meta Transaction, Bundlers bundle multiple UserOperations into one bundle (one native transaction)!
Reliably land userOps onchain with our Bundler API
5 Benefits of Account Abstraction over Meta Transactions
1. No Smart Contract Changes are Required
While Meta Transactions require updates to all existing contracts that would adopt them, Account Abstraction builds on existing infrastructure. This means that all smart contracts by default support Account Abstraction, which makes it a preferred option over Meta Transactions.
2. Frictionless Switching Between Bundler and Paymaster Services
Under ERC-4337, all Bundlers and Paymasters communicate following specific standards. Teams can even create their own Paymasters with conditional logic for their application.
3. No Need to Adopt Proprietary Relayers
Proprietary Relayers lack consistency; each Relayer can have their own message format for their use case. This leads to smart contract changes being required to become compatible with each different Relayer.
4. More Decentralization
As more providers make their Bundler services available, the developer gains the ability to decentralize their transaction flow. This also affords the developer the opportunity to abandon any sub-par Bundlers.
5. No Developer Tooling Lock-in
When using Meta Transactions you also need to use the Infra provider’s SDK. This leads to tooling lock-in that adds to the friction when migrating Relayers.
In the case of Account Abstraction, all the standard functionality is supported by all SDKs allowing one to select based on their expertise and switch based on preference!
Moreover, since the UserOperation standard is to be adopted by every vendor, building tools like UserOperation Explorers is also feasible.
How to Update Meta Transactions to Account Abstraction?
If you have already made changes to your smart contracts in order to support Meta Transactions, the migration process is simple to revert those changes.
Unlike Meta Transactions, msg.sender and msg.data can be used as-is with Account Abstraction.
If custom Paymasters or Account Factories are desired, their development becomes the next step in migrating.
For standard implementations, we recommended using well-audited, existing AA providers in order to reduce development time and self-imposed bugs.
Alchemy’s Gas Manager provides granular controls like Per Address Gas Usage limits, Max number of UserOperations to sponsor, Allowlisting addresses, Sponsorship deadlines, and Domain level allowlisting!
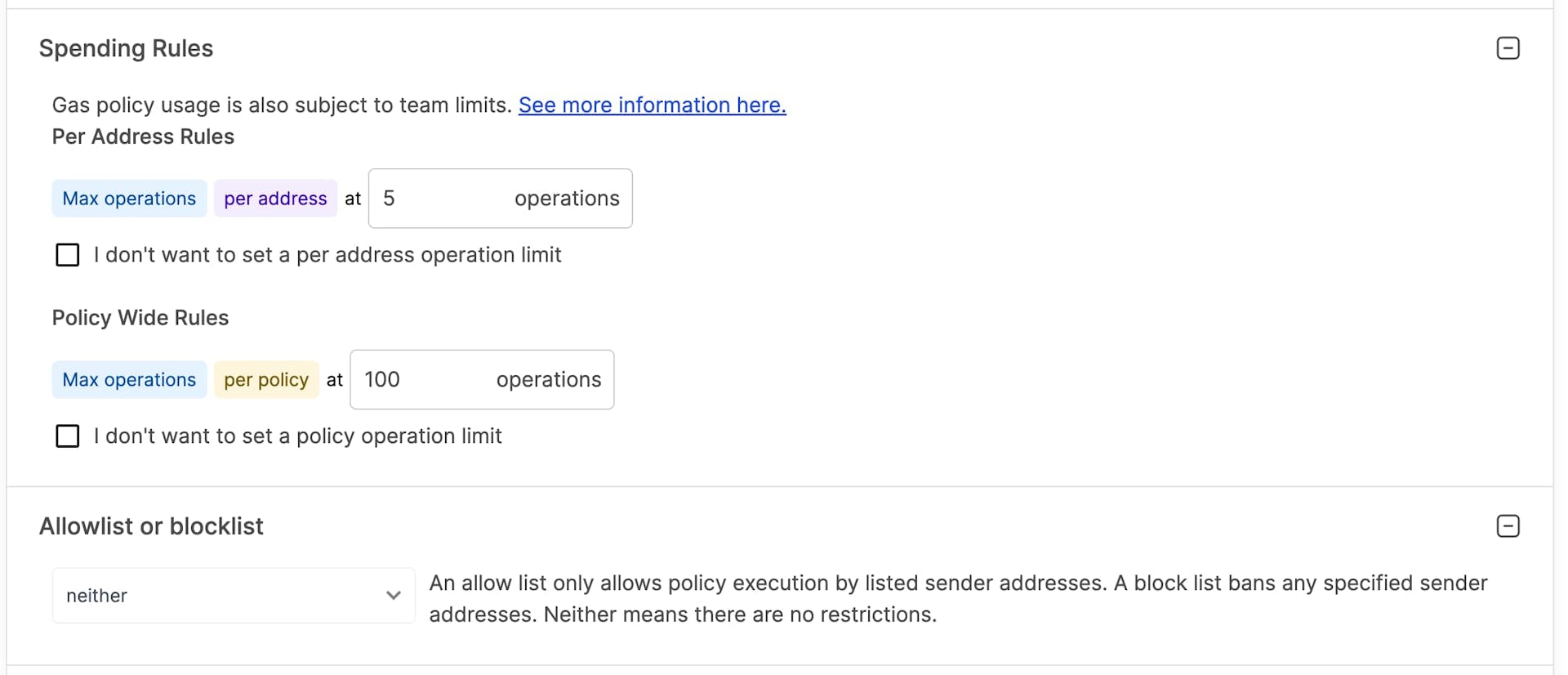
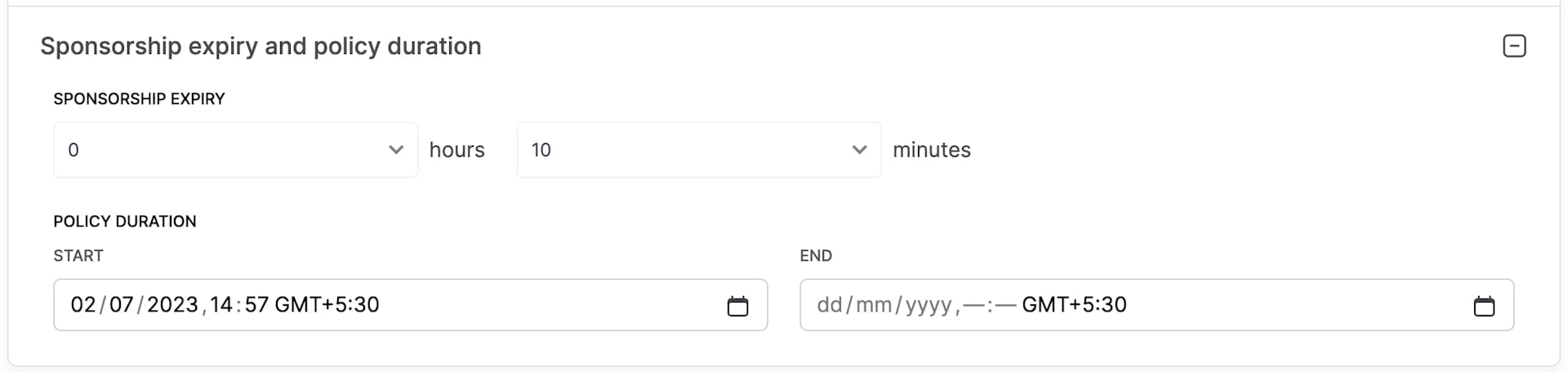
Gas Manager Admin API allow programmatically creating, reading and updating the Gas policies. On top of everything, the developer gets a great visual dashboard of every UserOperation sponsored!
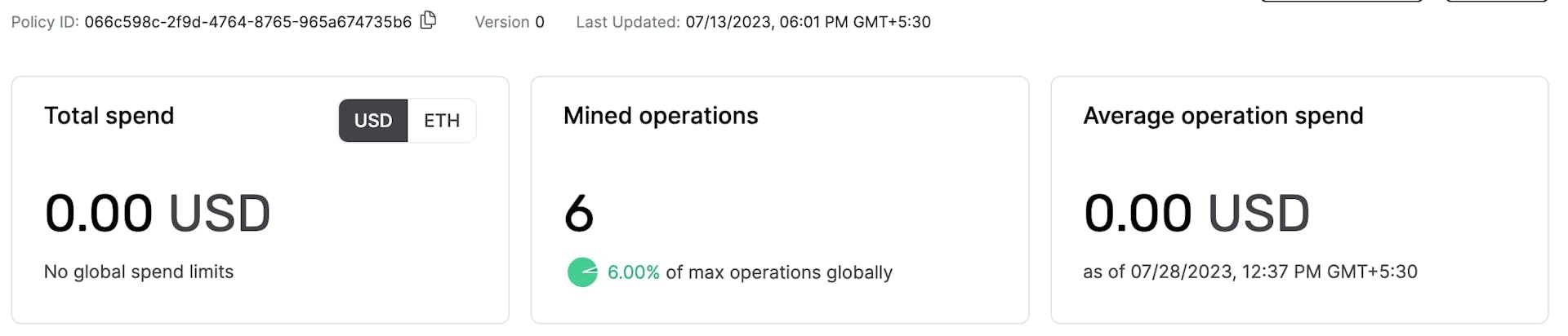
Conclusion
Account Abstraction (ERC-4337) is the new and better way of incorporating gasless transactions into your dapps with benefits like avoiding contract-level code changes, frictionless vendor switching, composability with other existing infrastructure, and more decentralization.

Related overviews
ERC-4337 enables smart contract wallets on Ethereum without requiring any consensus-layer protocol changes.
Build wallet infrastructure that hides blockchain complexity. No seed phrases, no gas fees, just easy login.
Learn web3 authentication basics and how to build modern flows onchain with email and social login.

Build blockchain magic
Alchemy combines the most powerful web3 developer products and tools with resources, community and legendary support.