
5 Reasons Why You Should Build on Polygon zkEVM
Written by Mustafa
Polygon zkEVM is a layer 2 blockchain that uses zero knowledge technology and validity proofs to increase Ethereum's scalability, reduce gas costs, and give developers a familiar development environment.
The difference between Polygon's Proof-of-Stake blockchain and Polygon zkEVM is that Polygon PoS is an Ethereum Sidechain and Polygon zkEVM is a native L2 rollup that is secured by Ethereum.
What is Polygon and Why Polygon zkEVM?
The Polygon network is designed to provide a layer 2 scaling solution for Ethereum, which means that it operates on top of the Ethereum network and allows for decentralized applications (dapps) to run faster and with lower fees. The project gained significant traction in the decentralized finance (DeFi) space in 2020 and 2021, as developers sought to build scalable applications that could handle large transaction volumes.
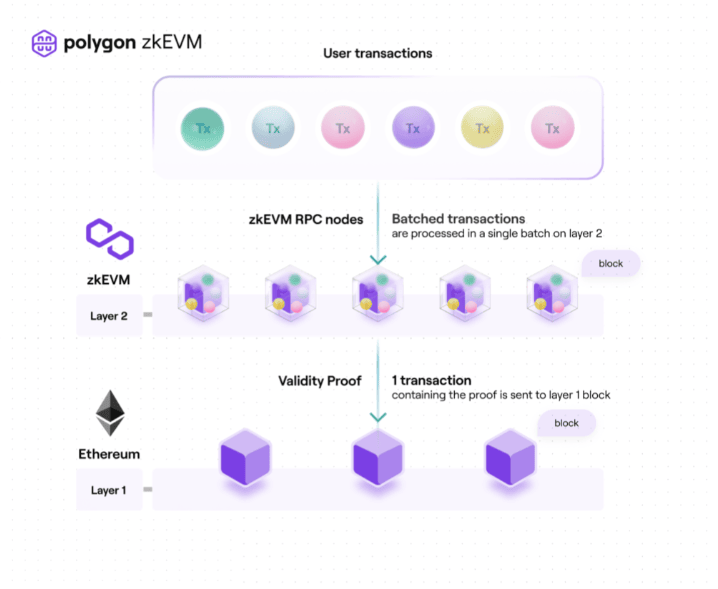
Polygon supports rollups as a layer 2 scaling solution. Rollups work by batching multiple transactions together into a single transaction and then submitting this batch to the main blockchain. This significantly reduces the number of transactions that need to be processed on the main chain, which in turn reduces the fees and processing time required for each transaction.
The blockchain industry recognizes two types of rollups: optimistic rollups and zk-rollups. Polygon zkEVM mainnet beta went live on March 27th, 2023.
Going forward, this article will focus on zkEVM rollups; also, ZK rollups and zkEVM will be used interchangeably to refer to Polygon zkEVM. The article will provide an explanation of zero-knowledge proofs later on.
To fully comprehend the concept of a zkEVM, it is essential to have a clear understanding of its constituent parts. At its core, a zkEVM is the fusion of two robust technologies - zero-knowledge proofs, a groundbreaking cryptographic solution, and the EVM, which can be described as a distributed state machine — it facilitates the hashing of smart contract states, creating a value associated with the contract account consistent with the Ethereum network’s consensus mechanism.
Why Developers Choose Polygon for Blockchain Development
The five main reasons why developers choose to deploy applications to Polygon's zkEVM network are Zero-knowledge, EVM equivalence, scalability, cost, and ecosystem.
1. ZK Proof Technology
Zero-knowledge (zk) is a cryptographic protocol that enhances security when generating proofs to validate a statement. The core principle is that a statement can be proven without revealing the information used to derive the solution. For a zero-knowledge proof to be valid, it must adhere to certain rules: the verifier should be convinced if and only if the statement is valid, and should be unconvinced when the statement is false. Moreover, the proof should be verifiable without revealing the statement that is being proved.
To aid in understanding the concept, an analogy will be utilized. In this scenario, two individuals named Alice and Bob each have their own secret numbers. A third party wants to prove to Alice and Bob that they know the sum of their two numbers without revealing either individual number.
The third party can begin by asking Alice and Bob to write their numbers on a piece of paper and place them inside a locked box. They can then request the locked box from Alice and Bob, but not the key to open it. The third party can then approach another friend with a calculator and ask them to add together the two numbers without disclosing what the individual numbers are. The third party can record the sum on a piece of paper.
Afterwards, the third party can provide Alice and Bob with the paper containing the sum and request that they verify if it is correct. Alice and Bob can then use their own numbers and a calculator to check the sum without revealing their individual numbers to each other. If the sum is correct, Alice and Bob will believe that the third party knows the sum of their numbers without having to disclose their individual numbers.
Polygon offers a cutting-edge ZK (Zero-Knowledge) proof solution, which utilizes the power of zero-knowledge proofs to ensure that all transactions happening on the network are valid. Imagine that Alice and Bob's numbers are their assets on the blockchain, and the third party is the blockchain proving to the world that transactions are valid, without revealing who owns what assets.
By leveraging this technology, Polygon enables developers to build decentralized applications that protect user privacy and ensure the integrity of the network.
2. EVM Equivalence
Polygon's zkEVM is a Layer 2 scaling solution for Ethereum that utilizes zero-knowledge proofs to enhance scalability while maintaining Ethereum compatibility. By using zkEVM, developers and users on Polygon can use the same code, tools, and applications they use on Ethereum but with significantly higher throughput and lower fees.
EVM-equivalence refers to the ability to compile code in the same way as Ethereum, allowing developers to launch their existing Ethereum-based applications on new chains instantly.
As an EVM-Equivalent chain, the Polygon zkEVM is a great choice for developers looking for instant scalability for their existing Ethereum dapps.
3. Scalability
Layer 2 protocols such as Polygon are well-suited for contracts that require frequent transactions, as they can group multiple transactions together for a single validation on the Ethereum mainnet.
To provide an example, imagine a decentralized exchange (DEX) which employs a smart contract to enable users to trade tokens with one another.
In a traditional scenario, every trade would necessitate a separate transaction on the Ethereum network, which can be very slow. However, by utilizing a layer 2 protocol such as Polygon, the DEX can combine numerous trades into a single batch for validation on the Ethereum mainnet. This is the core idea of a "Rollup".
This batch processing approach diminishes the number of required transactions and enables developers to scale their DEX application.
4. Cost
The zkEVM solution offered by Polygon uses a batch processing system. This significantly reduces transaction costs on the Ethereum network. By grouping multiple transactions together into batches, zkEVM is able to reduce the number of transactions required for each operation, which in turn reduces the gas fees associated with each transaction.
This cost-saving measure enables developers to create more affordable and accessible decentralized applications, such as decentralized exchanges and NFT marketplaces.
5. Ecosystem
The Ethereum developer ecosystem has been built over time with significant investment in resources and energy, and maintaining compatibility with this ecosystem is a major advantage of zkEVM. By leveraging the power of zkEVM, developers are not only scaling the number of transactions per second on the Ethereum network but also building on the strong foundation of a thriving community and ecosystem.
Start Developing on Polygon zkEVM
Polygon zkEVM is regarded as one of the most promising solutions to Ethereum's scalability challenges. With Polygon's dedication to incorporating ZK rollups, the possibility of scaling Ethereum is greatly enhanced. Alchemy is committed to advancing Ethereum's scalability helping developers start building on Polygon zkEVM.
To start building on Polygon, create a free Polygon zkEVM developer account with Alchemy today!

Related overviews
How can rollups help your business change its unit economics?
Discover how enterprises are bringing their business onchain.
Explore the tactics of MEV and how you can protect your users from unfair trade manipulation.

Build blockchain magic
Alchemy combines the most powerful web3 developer products and tools with resources, community and legendary support.