
How to Develop an NFT Viewer (5-Step Tutorial)
Written by Alchemy
One of the most prominent aspects of NFT smart contracts is that they do not include the artwork, images, or files themselves, but just links or URIs to them and their metadata. These tokens identify off-chain locations for such files and data, therefore the blockchain is not responsible for hosting this content.
As we will see in this next section, ERC-1155 is an improvement over ERC-721 in that its code works for both non-fungible and semi-fungible tokens (NFTs).
NFT Viewer Requirements
Node >= 16.13.x
Alchemy
React.js
TailwindCSS
NFT Viewer Tutorial
Here are the steps to create an NFT viewer dapp using Alchemy.
1. Clone the Repo
To clone the NFT Viewer repository, open up your terminal and run the following command:
git clone https://github.com/alchemyplatform/Build-Your-NFT-Explorer.git2. Install npm
NPM stands for "node package manager." To install npm, simply run this command from your terminal:
npm install3. Create an Alchemy Account on Alchemy
Create a new Alchemy account or create a new app if you're already an Alchemy developer.
Once you have your app, copy your API Key.
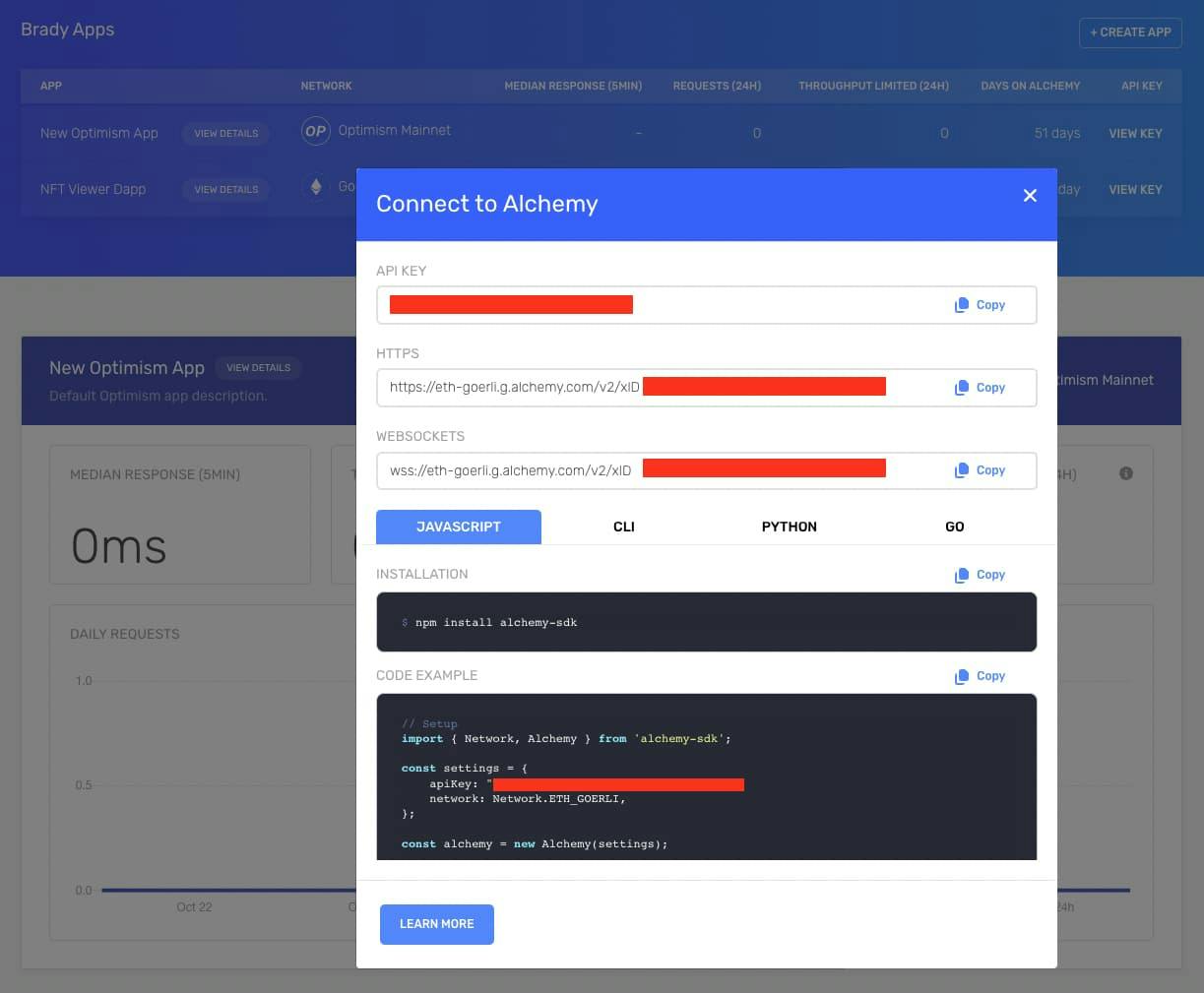
4. Replace your API Key in the fetNFTs.js file
From there update const apiKey = "demo"; in src/utils/fetchNFTs.js with your Alchemy API Key.
Then run this command in your terminal:
npm start5. Enter a wallet address
To view the owned NFTs of a given wallet address, simply enter the wallet's address string.
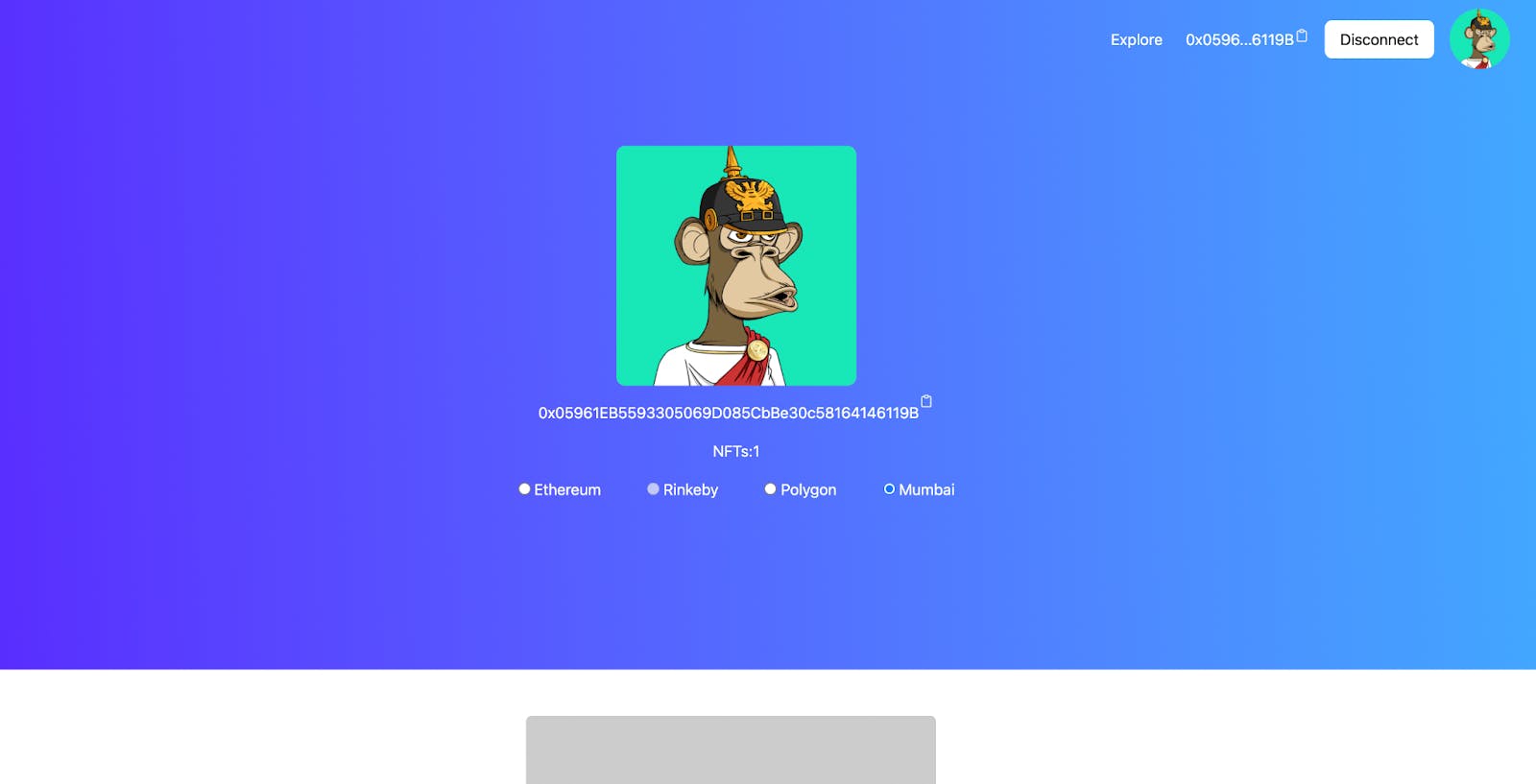
For more info on this tutorial refer to this video!
Using the Alchemy NFT API
The NFT API from Alchemy allows you to rapidly obtain all of the information you need about NFTs from the blockchain, and it works across Ethereum, Polygon, Arbitrum, Optimism, and Ethereum testnets.
Rather than manually scanning, indexing, and storing data, you can now submit a single request to retrieve particular NFT information for both ERC-721 and ERC-1155 tokens. This includes retrieving information such as finding all NFTs held by an address or metadata/attributes for a given NFT token.
For more information check out the NFT API documentation.
What are NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens)?
The term "NFT" refers to digital assets that represent real-world artifacts, such as art, music, or video game assets.
Even though they've only been around since 2014, the use of NFTs to purchase and sell digital artwork continues to grow in popularity. Today there are multiple smart contract implementations for NFTs on Ethereum with the two main token standards being ERC-721 and ERC-1155.
What are ERC-721 tokens?
Since their first release as an Ethereum Improvement Proposal (EIP) in September 2017, ERC721 tokens, also known as Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs), allow developers to tokenize ownership of any arbitrary data on the Ethereum blockchain.
ERC-721 defines the minimal interface that a smart contract must technically implement. This basic interface facilitates token ownership, trading, and administration. ERC-721 does not require a token-related information standard and does not exclude the installation of functions that exceed minimum requirements.
The ERC-721 token standard greatly expands the design space for tokens. Because each non-fungible token is linked to a distinct identity, they are all unique to their owner. Tokens adhering to the ERC-20 token standard on the other hand are fungible, meaning they may be used interchangeably.
Dieter Shirley, the chief technology officer at Dapper Labs, designed ERC-721 as a draft EIP (Ethereum Improvement Proposal), which ultimately served as the foundation for the game CryptoKitties. Other ERC-721 authors include William Entriken, Jacob Evans, and Nastassia Sachs.
What are ERC-1155s?
The ERC-1155 token standard is for semi-fungible tokens, and was created by a team of developers at Enjin to solve the limitations of ERC20 and ERC721 tokens.
Previously, a separate contract was needed for each fungible or non-fungible currency under ERC-20 or ERC-721 respectively. In addition, older standards restricted certain capabilities by dividing each contract into a separate address. As a result, the Ethereum blockchain is littered with unused bytecode.
Conclusion
Although NFTs are still in their infancy, they are presenting artists with extraordinary benefits like digital ownership, new revenue streams, and enhanced community engagement.
To continue learning about NFT dapps, explore related tutorials such as:

Related overviews
Learn how Japan's government is accelerating innovation and how companies are using blockchain technology.
Japan Airlines and Calbee, a Japanese Snack Food company, are using NFTs to promote tourism and brand loyalty.
WaveHack is the biggest web3 hackathon in Japan, and is being held from mid-April to the end of August 2024.

Build blockchain magic
Alchemy combines the most powerful web3 developer products and tools with resources, community and legendary support.