
What is the Solidity compiler?
Written by Daniel Idowu
Ethereum developers writing smart contracts in Solidity must run their code through a compiler so that the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) can understand and execute appropriate commands. The Solidity compiler converts the code to a collection of byte instructions.
Solidity is the programming language for Ethereum, the second-largest cryptocurrency by market capitalization. Solidity is a high-level programming language created specifically for putting smart contracts into action. Additionally, Solidity is a contract-oriented and object-oriented language with statically-typed objects.
In this article, we will walk you through the Solidity compiler, how to install Solidity compilers, Solidity compiler tools, and even decompilers that are publicly available.
What is the Solidity compiler?
There are two Solidity compilers: solc and solc.js, which is derived from solc. The actual Solidity compiler, solc, is written in C++ and is at version 0.8.16 at the time of this article. Solc.js uses Emscripten to compile the C++ code into JavaScript. Solc is compiled into JavaScript for every version.
Solidity files are assembled using the Node.js library and command-line tool known as solcjs. It uses only JavaScript for compilation rather than the solc command-line compiler, making it simpler to install than solc.
Before smart contracts can be deployed they must be compiled to bytecode for the EVM (Ethereum Virtual Machine). Bytecode is the information that Solidity code is "translated" into, and it contains binary computer instructions.
In Ethereum, the bytecode is what is deployed to the blockchain. The compilation also generates an ABI (Application Binary Interface) which is an interface between two program modules, often between operating systems and user programs.
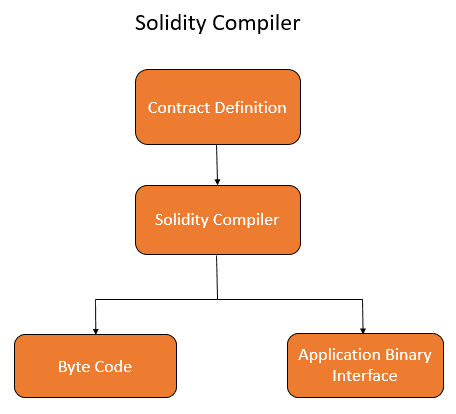
Contracts are compiled into bytecode that is executed on the EVM. This bytecode is deployed to the blockchain and saved at an address. It is then made public and available for anyone to interact with. An address identifies a deployed contract instance, which also holds persistent storage for maintaining the contract's internal state. Ether, Ethereum's native cryptocurrency, is used as a store of value, a method of payment for executing smart contracts on the blockchain, and a reward for miners who keep the Ethereum network secure.
The following is a quick example of how a contract is compiled.
We will be compiling this code using Remix, a popular online Ethereum IDE, so we do not have to install any tools to our local machine.
//SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
contract Greeter {
string greeting;
constructor(string memory _greeting) {
greeting = _greeting;
}
function greet() public view returns (string memory) {
return greeting;
}
function setGreeting(string memory _greeting) public {
greeting = _greeting;
}
}
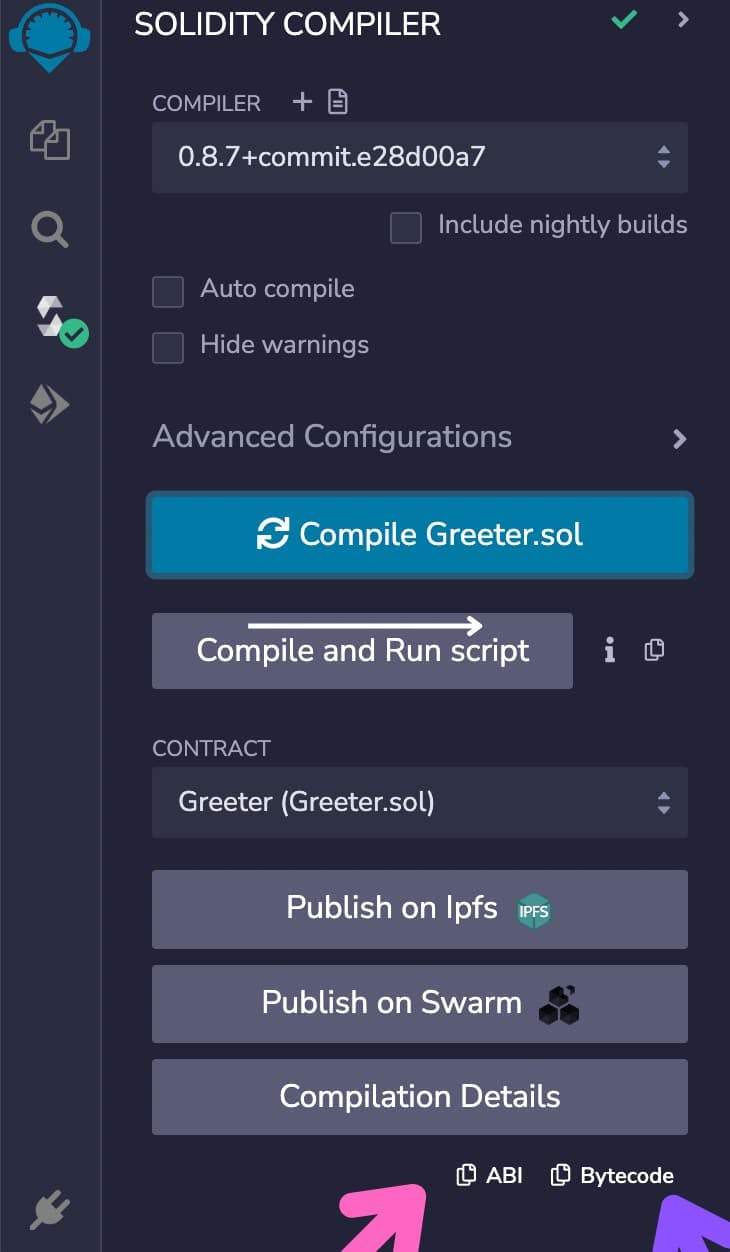
From the image below, you should notice the pink and purple arrows at the bottom of the image pointing to the ABI and the bytecode respectively. ABIs are represented as JSON.
How to Install the Solidity Compiler
While learning Solidity, you may want to install a Solidity compiler. There are various convenient ways of installing the Solidity compiler. An easy method is to use Remix, where you have the option of using it online and. However, this is designed for small contracts and has little compilation options.
For larger contracts you can install the Solidity compiler using npm/Node.js, Docker, Linus, MacOS packages and from static binaries.
Method 1: Install Using npm/Node.js
The Solidity compiler also known as solc can be installed using npm. The command below will install the solcjs program and make it available throughout the system.
npm install -g solc
You can now test your Solidity compiler by running the following command.
solcjs --version
You are now ready to use solcjs, which has fewer features than the standard Solidity compiler but will provide you with a good starting point.
Method 2: Install Using Docker
To get started with Solidity programming, you can download a Docker image and use it. Because the Docker image runs the compiler executable, you can pass it any compiler arguments.
The command to pull a Solidity Docker Image is as follows.
docker pull ethereum/solc
After downloading a Docker image, run the following command to verify it.
docker run ethereum/solc:stable -version
To compile Solidity files on the host machine using the Docker image, mount a local folder for input and output and specify the contract to compile.
docker run -v /local/path:/sources ethereum/solc:stable -o /sources/output --abi --bin /sources/Contract.sol
Method 3: Install Using Binary Packages (MacOS, Linux)
MacOS Installation
We can use Homebrew to install Solidity on MacOS. This provides us with built-from-source macOS packages, and we simply need to follow the installation instructions.
brew update
brew upgrade
brew tap ethereum/ethereum
brew install solidity
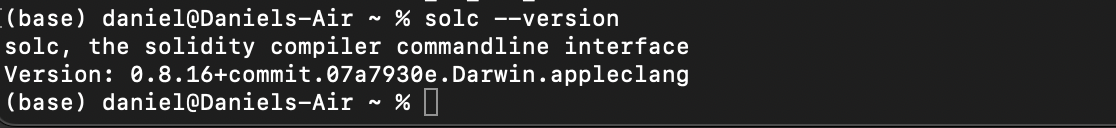
After the execution has completed, we can verify that Solidity has been successfully installed running the command below.
solcjs --version
You should receive an output like this:
Linux Installation
Installing Linux packages is a very simple procedure that can be completed in just a few steps. First, add the repository to our repository list.
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:ethereum/ethereum
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install solc
Then Update the package list and install solc. If we want to use the nightly build instead of the latest stable release, we should change the repository entry to ethereum/ethereum-dev.
Compiling a Sample Solidity Smart Contract
The following code uses our sample contract provided above.
//SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
contract Greeter {
string greeting;
constructor(string memory _greeting) {
greeting = _greeting;
}
function greet() public view returns (string memory) {
return greeting;
}
function setGreeting(string memory _greeting) public {
greeting = _greeting;
}
}
To compile a contract we can run the following code.
solc Greeter.sol
To use a specific EVM-version to compile our contract, we can set the version as follows.
solc --evm-version [EVM-VERSION] contract.sol
What is solidity-upgrade?
The solidity-upgrade allows you to upgrade your contracts to reflect breaking language changes. While it does not and cannot make all the necessary adjustments for every breaking release, it nevertheless supports the ones that would otherwise require a lot of tedious manual adjustments.
How does solidity-upgrade work?
Solidity-upgrade, which is based on libsolidity, can parse, compile, and analyze your source files in order to find applicable source upgrades. Source upgrades are regarded as minor textual alterations to your source code. They are applied to an in-memory replica of the provided source files.
The upgrade has two phases:
First phase
Firstly, since it is not possible to upgrade source code at that level during the parsing of source files, errors are gathered and can be logged by giving the —verbose flag. There are currently no source upgrades available.
Second phase
In the second phase, all sources are compiled and all activated upgrade analysis modules are run alongside compilation. By default, all available modules are activated.
Compilation issues may emerge from solidity-upgrade, which source updates are potentially able to fix. If there are no problems, there are no source upgrades being reported, and you are finished. If issues happen and a source upgrade was reported by an upgrade module, the first reported source upgrade is applied and recompilation is initiated for all provided source files.
What is a Solidity decompiler?
The Solidity decompiler is a tool that takes compiled smart contract EVM code as input and decompiles it to Solidity-like source code. The decompiler helps in verifying and understanding the behavior of contracts.
The Solidity decompiler is useful in debugging smart contracts where the original code is unavailable. However, the technology behind decompiling EVM bytecode is still in development as some of the decompilers available only partially decompile complex contracts, with much of the low-level code frequently missing from the decompiled version.
Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) decompilers
Here is a list of popular Solidity decompilers:
1. Ethervm.io
Ethervm.io is a free online decompiler that decompiles Ethereum contract bytecode into more readable Solidity-like code.
Get started: https://ethervm.io/decompile
2. JEB Decompiler
The JEB decompiler provides specific capabilities such as code analysis to determine methods without access to an ABI. JEB has become the preferred tool for security auditors, vulnerability researchers, and reverse engineers investigating opaque smart contracts running on Ethereum platforms.
Get started: https://www.pnfsoftware.com/jeb/manual/ethereum/
3. Etherscan Online Decompiler
The Etherscan online decompiler is a decompiler for the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) that extracts information from Runtime bytecode and presents it in a more human-readable format.
4. Evemedis by Nick Johnson
Evemedis is an EVM disassembler. It performs static analysis on the bytecode in order to provide a higher level of abstraction than raw EVM operations.
Get started: https://github.com/Arachnid/evmdis
5. Decurity
Decurity is an ABI decompiler that implements simple tools for recovering EVM smart contract ABI, including function names.
Get started: https://github.com/Decurity/abi-decompiler
Final Thoughts
Now you understand what Solidity compilers are, how to install them and how to compile a simple contract. The Solidity documentation contains more information on Solidity compilers.
If you’re just starting to learn Solidity, secure your spot in Alchemy University's 7-week Solidity developer bootcamp to master the fundamentals of Ethereum development in a free, interactive, and comprehensive online course. If developers are new to development in general, Alchemy University's 3-week JavaScript crash course is a great prerequisite before starting an Ethereum bootcamp. If you've got the basics covered and want to dive deep, check out Alchemy's new Solidity Course

Related overviews
Explore the best IDEs for Solidity development.
Want to write better code and lower your gas fees?
Secure your smart contracts with these expert security tips and tools.

Build blockchain magic
Alchemy combines the most powerful web3 developer products and tools with resources, community and legendary support.