
Ethereum Sidechains vs Layer 2s: What’s the Difference?
Written by Alchemy
With millions of users joining the Ethereum network and developers building Ethereum applications every day, Ethereum is limited by the number of its transactions. Ethereum’s capacity to process transactions, its transaction throughput, is limited to 15 transactions/second, leading it to become increasingly expensive and often too congested for many people to use.
The Ethereum network is the main chain, and all transactions that occur directly on it are “on-chain”, while anything else is considered “off-chain”. It’s some of these off-chain solutions like sidechains and layer 2s that could help Ethereum scale, increasing transaction speed and increasing the amount of transaction data the network can handle. In this article, we’ll show you what sidechains and layer 2 solutions are and how they can help with scalability.
What problems do sidechains and layer 2s solve?
Sidechains and layer 2 Ethereum solutions tackle the problem of helping Ethereum scale. Attempts to try to scale up performance on-chain often lead to trading off either the decentralization or scalability of Ethereum - this is known as the Scalability Trilemma.
Increasing the sophistication of Ethereum layer 1 is not ideal as it would heighten the level of governance overhead for the platform to continuously debate, decide and implement new improvements. Sidechains and layer 2 solutions allow for constant and incremental innovation that improves Ethereum for everyone while maintaining security and decentralization.
What’s the main difference between sidechains and layer 2 solutions?
The main difference between sidechains and Ethereum layer 2 solutions is that while layer 2 inherits the security of the main Ethereum network, sidechains rely on their own security.
What is an Ethereum side chain?
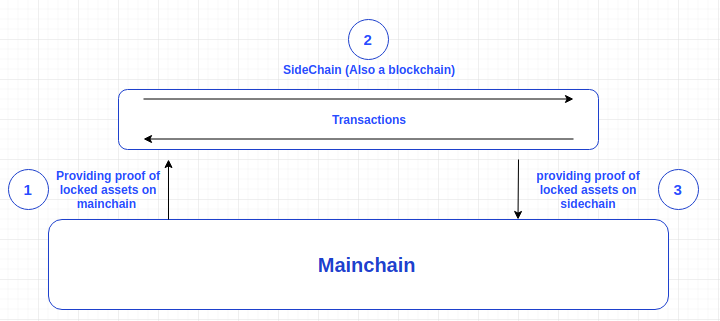
An Ethereum sidechain is a separate blockchain network that runs in parallel to the Ethereum main chain. Sidechains connect to the main chain via a two-way peg system allowing assets to be exchanged between the chains.
There are two basic types of sidechains, one in which a chain is dependent on the other and another where they are independent.
When one chain is dependent on another chain like Ethereum, it can be considered the child chain of this parent chain. Typically, the child chain doesn’t create its own assets and derives any assets from transfers from the parent chain.
Sidechains have their own consensus protocols that are often designed for specific kinds of transactions and allow them to be faster and more affordable. However, this also means that they don’t typically inherit the security properties of Ethereum and when using a sidechain you lose custody of your funds and rely solely on the side chain’s security, including the nodes participating in its own consensus protocol.
Sidechains reduce the congestion on the main chain, reducing the cost for everyone and increasing the usability and scalability of the Ethereum ecosystem. Developers can also use sidechains to explore and test new features and use cases that are not available on the main chain.
Popular sidechains include Polygon PoS, Skale, and Rootstock. Ethereum 2.0 has its own variation of sidechains called shard chains that are attached to the recently launched Beacon Chain, which aims to ultimately become the main chain of proof of stake (PoS)-based Ethereum.
How do sidechains work?
Sidechains work by connecting to the main chain through a two-way-peg system or bridge. From the main chain, you can send your Ethereum to an exit address that acts as a lockbox so that you’re not able to spend it elsewhere.
Once this transaction is completed and the “contest period”, for additional security, has passed, then a receipt called the “Simple Payment Verification” (SPV) is provided. This triggers the release of the same value from a lockbox on the side chain via a smart contract. When “transferring” from the side chain back onto the main chain, the exact same process happens but in reverse.
How to develop on sidechains?
Sidechains are based on the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), which is the computation engine for Ethereum, and this compatibility with the Ethereum Virtual Machine means developers don’t need to make any changes when they want to use their application in a sidechain. It’s simply a matter of deploying the same code because they all share the same software layer of Solidity and can be accessed through the same Web3 API!
What is layer 2 protocol?
Layer 2 protocols are chains that live inside the Ethereum chain but are able to achieve greater scalability through a secondary framework. This reduces congestion on the main layer by having the bulk of activity processed through the second layer. Unlike a sidechain, layer 2 generally inherits the security properties of the main chain.
Layer 1 is the base blockchain. Ethereum is a layer 1 blockchain because it is the underlying foundation on top of which various layer 2 blockchains are built. Simply put, layer 2 compresses bundles of transactions and submits them to the main Ethereum network.
What are layer 2 scaling solutions?
Layer 2 scaling solutions include channels, rollups, and plasma. Here’s a breakdown of each of these individual solutions.
1. State Channels
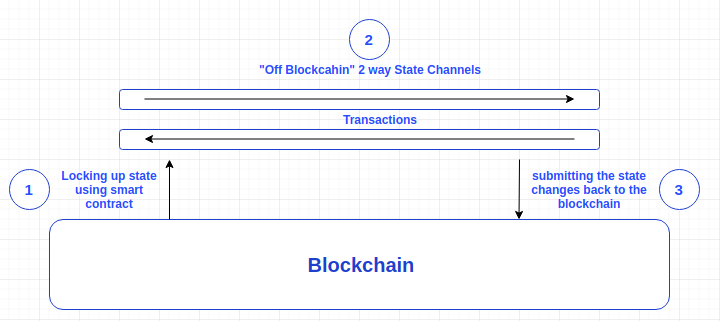
With state channels, users transact with one another directly off-chain and reduce on-chain transactions to only the most important information. Specifically, part of the blockchain is locked via a smart contract so that the participants involved in the transaction have to completely agree before updating it.
Participants update the state among themselves by creating and signing transactions that could be submitted to the blockchain. Once you want to stop using the channel, you exit and submit the last state update to the main chain which unlocks the state again.
2. Rollups
A rollup performs transaction execution off the main Ethereum blockchain and then batches together multiple transactions before sending them back to the main Ethereum network. Rollups rely on proofs to allow Ethereum to verify their correctness without processing transactions.
What are the two types of rollups?
In general, there are two types of rollups, Zero-knowledge (ZK) Rollups and Optimistic Rollups.
1. Zero-Knowledge Rollups (ZK rollups)
Zero-Knowledge Rollups (ZK rollups) use validity proofs. Every batch of transactions includes a cryptographic proof called a Succinct Non-Interactive Argument of Knowledge (SNARK) that is verified by a contract on the main Ethereum layer.
Since just the validity proof and not the bulky transaction data needs to be stored on the main chain, this computation off-chain saves large amounts of processing time and power, making zero-knowledge rollups faster and much more efficient.
2. Optimistic Rollups
Optimistic Rollups use fraud proofs. As the name suggests, these optimistically assume all transactions are valid and submit batches without any initial proof. There is a challenge period in which others are able to detect and prove that the data in a batch is fraudulent.
If the batch turns out to be fraudulent, Optimistic rollups execute a fraud proof and runs the correct transaction computation using the data available on the main Ethereum chain. Making it a requirement that participants stake ETH that is rewarded or slashed based on their actions incentivizes good behavior.
Companies like Optimism help Ethereum scale by offering greater throughput, lower latency, and lower gas fees. At the time of writing, Optimism gas fees are up to 10x cheaper than Ethereum!
3. Plasma
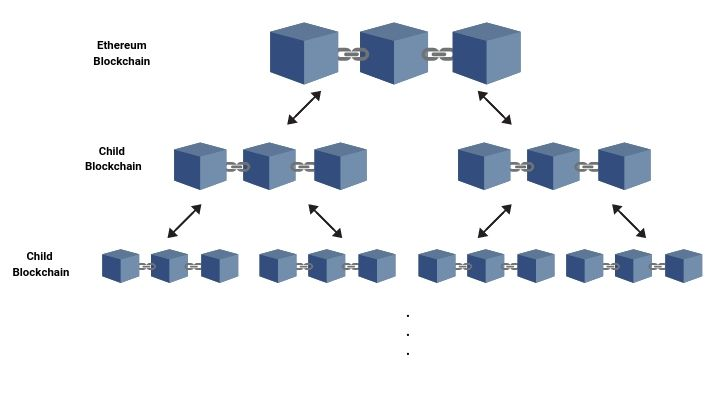
Think of Plasma as Ethereum’s native sidechain, using a combination of smart contracts and Merkle trees to create a limitless branching of child chains. These child chains are smaller copies of the Ethereum main chain with their own consensus mechanism.
The bandwidth needed for computation and the transaction data is offloaded from the parent chains but posted to the root chain at regular intervals. Each child chain relies on a proof of fraud system for security that is similar to rollups with a time period where anyone can challenge its validity.
The key difference from other sidechains is that the “root” of each plasma chain block is published to Ethereum, meaning it does inherit the main chain’s security.
Companies like Polygon enable faster transactions with much lower gas fees to developers and end users alike. These clear benefits make it incredibly enticing to build on plasma, and it’s easy to see why they have seen explosive growth.
What sidechains and layer 2s does Alchemy support?
Get a free Alchemy developer account to start building on Ethereum or these sidechains and Ethereum layer 2s:
Polygon (Sidechain)
Arbitrum (Layer 2)
Optimism (Layer 2)
Starknet (Layer 2)
Mass adoption of the implementation of scaling solutions like sidechains and layer 2 (channels, optimistic rollup, zk rollup, and Plasma) takes stress off the Ethereum mainnet and therefore helps more users speed up slower transaction times and lower high transaction fees while still maintaining the same security guarantees (in the case of Layer 2 solutions) and decentralized apps so well known to Ethereum.

Related overviews
How can rollups help your business change its unit economics?
Discover how enterprises are bringing their business onchain.
Explore the tactics of MEV and how you can protect your users from unfair trade manipulation.

Build blockchain magic
Alchemy combines the most powerful web3 developer products and tools with resources, community and legendary support.