
What Are Testnets?
Written by Alchemy
As more funds and users are onboarded to Web3 and decentralized finance (DeFi) services, security and reliability are becoming increasingly important for developers. Testnets are used by developers to ensure that the smart contracts and dApps (Decentralized Applications) they deploy are functional and secure.
Developers can work with the same clients as they would on the mainnet but testnets operate on a separate ledger. This separation creates a low-risk environment where developers can test and experiment without the costs of deploying on the mainnet.
Let's look deeper into what are testnets, the benefits of using a testnet, and how developers can access them.
What are testnets?
Testnets are test blockchain networks that act and perform similarly to the main networks (mainnets) they are associated with. Since they operate on separate ledgers from the mainnet, the coins on a testnet have no connection to transactions and value on the mainnet. This allows developers to deploy, test, and execute their projects on a functioning blockchain freely.
The cost of failure or mistakes on a mainnet is very high and at times irreversible so developers need an environment where they can comfortably work without these risks.
Security is a high priority for developers working on any decentralized platform. Operating on a testnet also offers the benefit of both investigating any vulnerabilities in the platform as well as educating developers on how the platform works. For testnets that are for pre-network upgrades, it is important to investigate how newly developed changes function before they are merged with the mainnet.
Differences Between Mainnets and Testnets
Most testnets have separate wallet systems to make it easier to manage coins and transactions outside of the mainnet. When deploying contracts and using services like Alchemy, testnets have distinct Network IDs .
For example, on the Ethereum network, the mainnet and testnets have the following IDs:
Ethereum mainnet - 1
Sepolia testnet - 11155111
Ropsten testnet - 3 (deprecated)
Rinkeby testnet - 4 (deprecated)
Goerli testnet - 5 (deprecated)
Kovan testnet - 42 (deprecated)
These IDs are used to ensure that the contract is deployed to the correct network and that the correct wallet system is used. Testnets do not experience the same amount of transaction frequency compared to their mainnets. Code is also not published publicly on testnets due to their changing nature compared to mainnets.
Ethereum Testnets
There are many different Ethereum testnets, including the newly introduced Sepolia.
Note: Ropsten, Kovan, and Rinkeby testnets have already been deprecated by the Ethereum Foundation. Additionally, While you can use the Goerli testnet, we caution against it as the Ethereum Foundation has announced that Goerli will soon be deprecated. Therefore, we recommend using Sepolia testnet as Alchemy has full Sepolia support and a free Sepolia faucet.
Sepolia
Sepolia is a proof-of-authority testnet created in October 2021 by Ethereum core developers and maintained ever since.
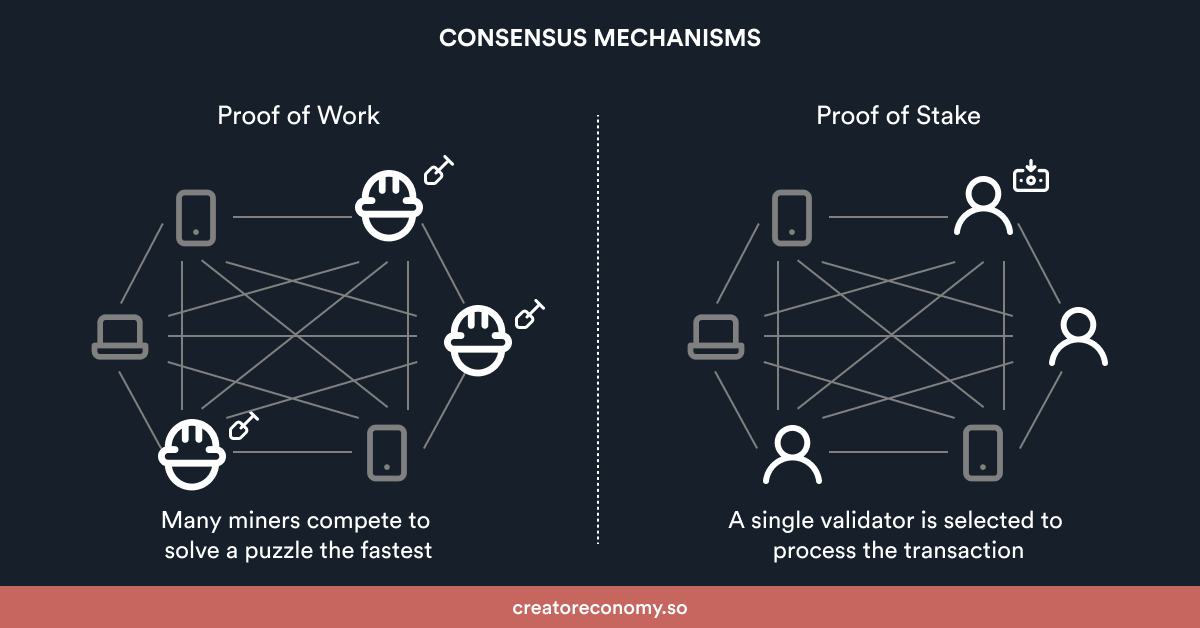
After the Ropsten testnet reached a Terminal Total Difficulty (TTD) of 50000000000000000 the Sepolia and the Goerli testnets transitioned to a proof-of-stake consensus mechanism to mimic the Ethereum mainnet.
Sepolia was designed to simulate harsh network conditions, and has shorter block times, which enable faster transaction confirmation times and feedback for developers.
Compared to other testnets like Goerli, Sepolia's total number of testnet tokens is uncapped, which means it is less likely that developers using Sepolia will face testnet token scarcity like Goerli.
Transactions can be viewed on Etherscan and Alchemy also offers a free Sepolia faucet. Due to the future deprecation of the Goerli testnet, we recommend Sepolia as the best testnet to use.
Ropsten (Deprecated)
The Ropsten testnet was launched in November 2016 and supports both Geth and Parity Ethereum node software.
Ropsten testnet allowed developers to use a highly authentic testnet to work on but also opens the network to attacks that would be very expensive to perform on the Ethereum mainnet. One of these happened in February 2017 when attackers deployed a high volume of complex transactions on the network to bring it down. The network was later brought back up and safeguards were put in place to prevent similar attacks.
Kovan (Deprecated)
After the attack on the Ropsten network, there was a need for an alternative testnets. Kovan launched in March 2017 to fulfill this need. The main difference between Ropsten and Kovan is their consensus models.
Kovan uses a Proof-of-Authority (PoA) model in which only specific nodes are authorized to confirm transactions and add any new blocks. Since the Parity team created this testnet, developers can only access it using the Parity node software.
Rinkeby (Deprecated)
Following the launch of Kovan, the Rinkeby testnet was launched in 2017 by the Ethereum team. Like Kovan, this testnet uses a modified PoA consensus model to confirm transactions. Unlike Kovan, the network only supports the Geth software and not Parity.
Goerli (Deprecated)
Goerli is a testnet that combines both a PoA consensus mechanism with wider support of node software compared to Rinkeby and Kovan. Goerli supports both Geth and Parity as well as Nethermind and Hyperledger.
With this higher level of support, the popularity of Goerli has been increasing. It is also the first testnet that was attempted to be moved to the proof-of-stake mechanism before running into issues after multiple attempts.
Transactions can be viewed on Etherscan and Alchemy also offers a Goerli faucet.
Morden / Kiln - the past and the future
Morden was the very first Ethereum testnet. Ethereum shut it down in November 2016, because the network experienced several attacks and became highly congested with useless data that affected performance.
The Kiln testnet was the last planned testnet before other Ethereum testnets and mainnet moved to a Proof-of-Stake consensus mechanism.
Ethereum created this testnet to allow node operators and developers to test before the company upgraded their other public Ethereum testnets.
Conclusion
Utilizing testnets is a critical step in developing applications on any blockchain network, and to ensure the growth of Web3, developers and users need to feel confident in the smart contracts and applications they use.
Testnets are key blockchain developer tools for creating the security and stability that users will increasingly demand as the growth of Web3 applications continues.
Want to start building decentralized applications on Ethereum testnets? Create a free Alchemy developer account to start building!
Frequently Asked Questions
What are testnets?
Testnets are test blockchain networks that act and perform similarly to mainnets but operate on separate ledgers, allowing developers to deploy, test, and execute projects without the risks and costs of using the mainnet.
What is the difference between a testnet and a mainnet?
Testnets operate on separate ledgers from mainnets, use simulated tokens with no real value, and allow developers to test safely, while mainnets handle live transactions with actual cryptocurrency assets.
Are testnet tokens worth anything?
No, testnet tokens have no connection to transactions and value on the mainnet and hold no real-world monetary value.
Why do developers use testnets?
Developers use testnets to ensure their smart contracts and dApps are functional and secure before deploying to mainnet, creating a low-risk environment for testing and experimentation.
Which Ethereum testnet should I use?
Alchemy recommends using Sepolia testnet, as many other Ethereum testnets like Ropsten, Kovan, Rinkeby have been deprecated and Goerli will soon be deprecated by the Ethereum Foundation.
What makes Sepolia different from other testnets?
Sepolia has shorter block times for faster transaction confirmation, simulates harsh network conditions, and has an uncapped number of testnet tokens, making it less likely for developers to face token scarcity.
How do testnets improve blockchain security?
Testnets allow developers to investigate vulnerabilities, test network upgrades, and identify issues before deploying to mainnet, where the cost of failure would be very high and potentially irreversible.
Can anyone access testnets?
Yes, testnets are accessible to developers who need to test their applications, and services like Alchemy provide free faucets to obtain testnet tokens for experimentation.

Related overviews
Building on Base? Get free Sepolia ETH and start testing your app!
Learn How to Migrate to the New Ethereum Testnet Sepolia From Goerli
Migrating dApps and Bridging Goerli ETH to Optimism

Build blockchain magic
Alchemy combines the most powerful web3 developer products and tools with resources, community and legendary support.