
What is an Ethereum node?
Written by Alchemy
Definition and Application
An Ethereum node is simply any computer running the software needed to connect with the Ethereum network. Nodes connect with one another to send information back and forth to validate transactions and store data about the state of the blockchain.
Though the terms are often used interchangeably these connected computers are the nodes and the software that they run is called the client.
Why are nodes important to Web3?
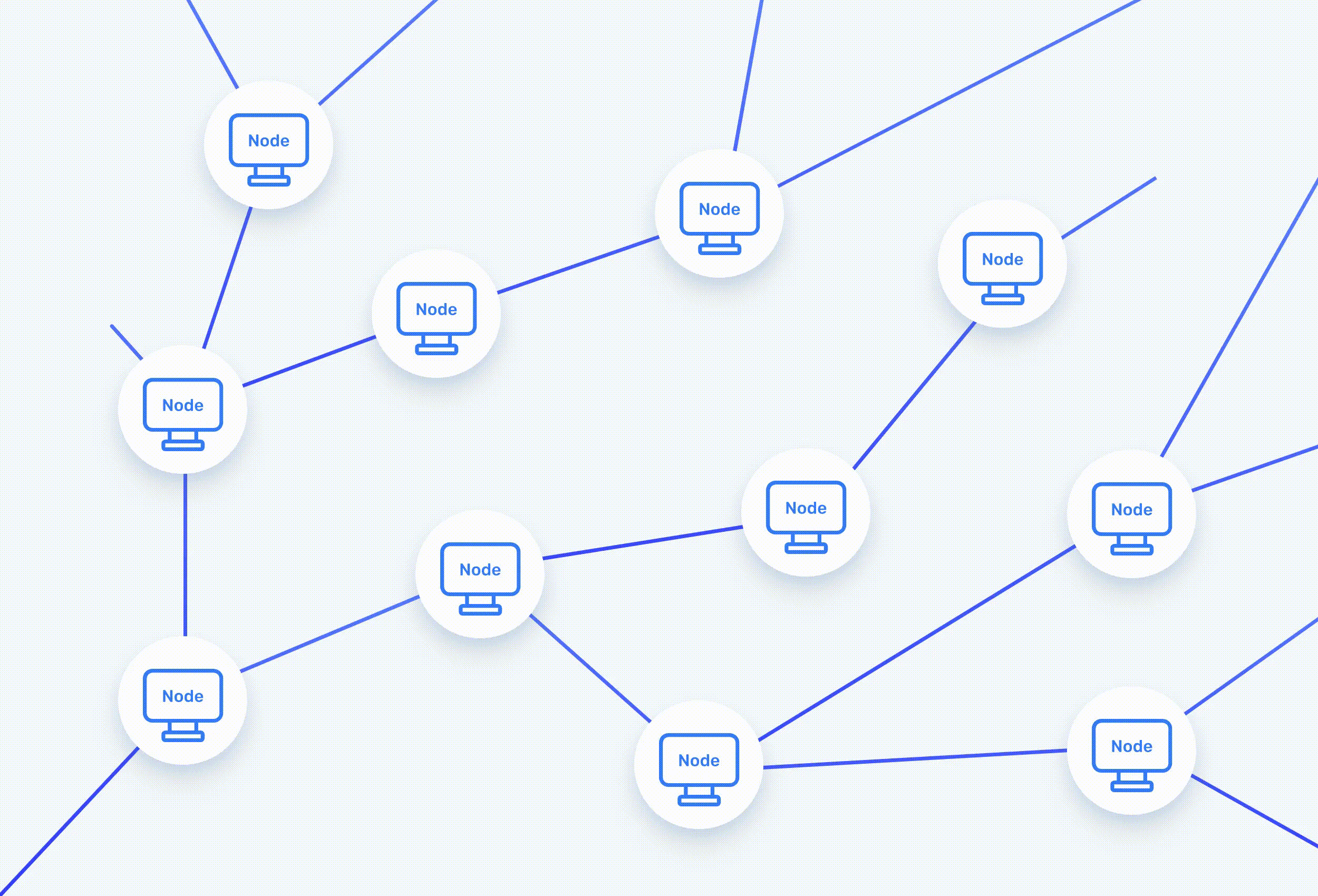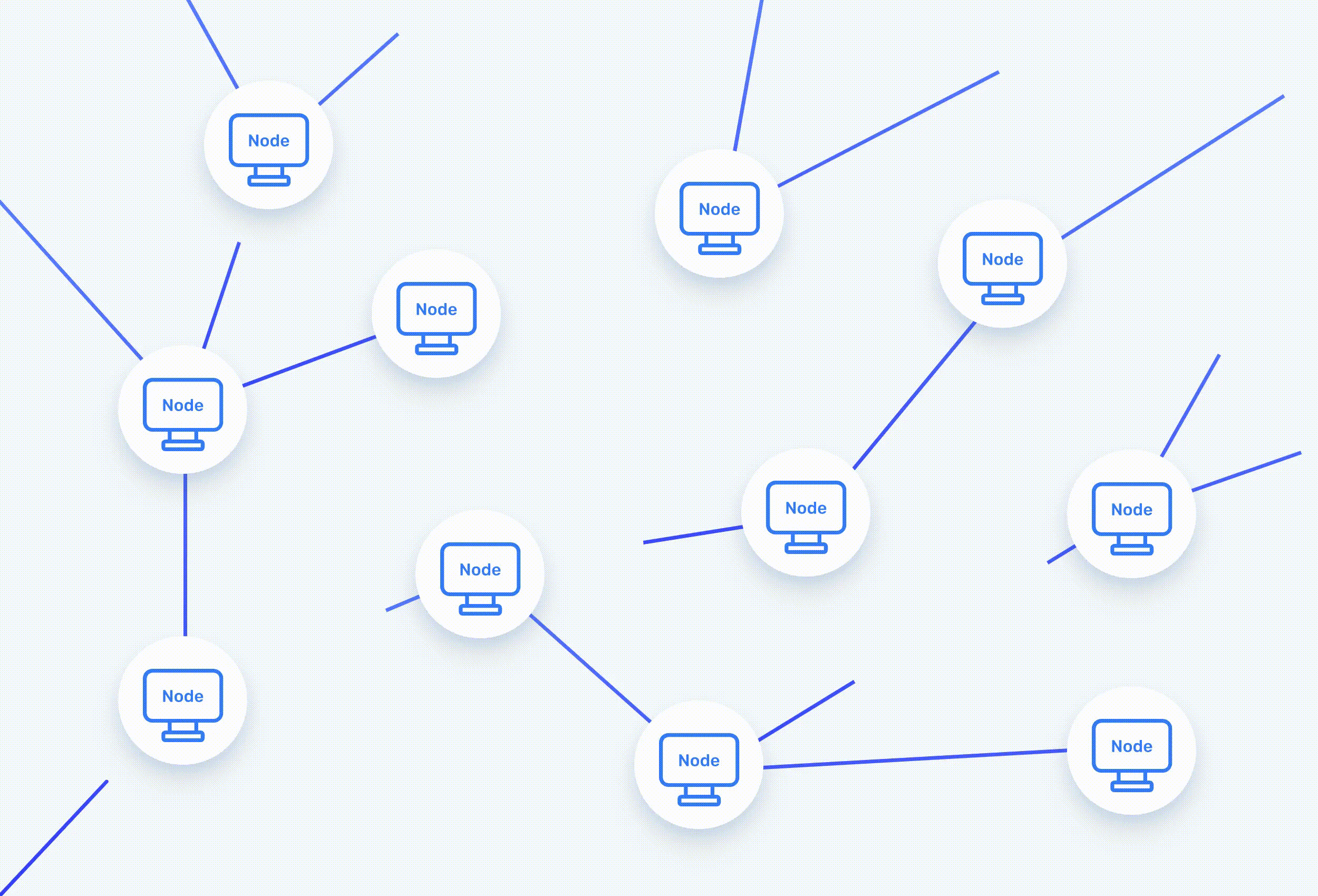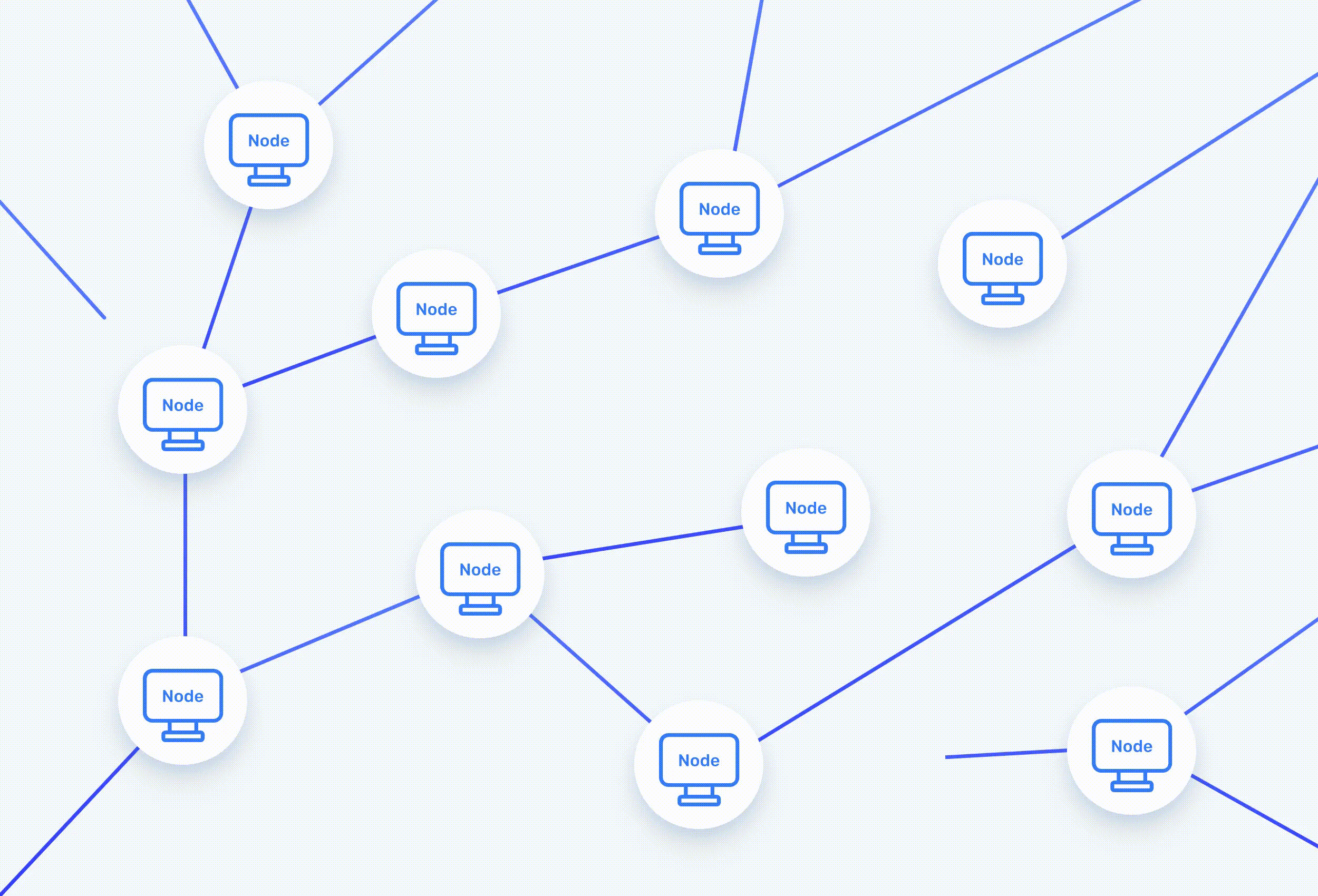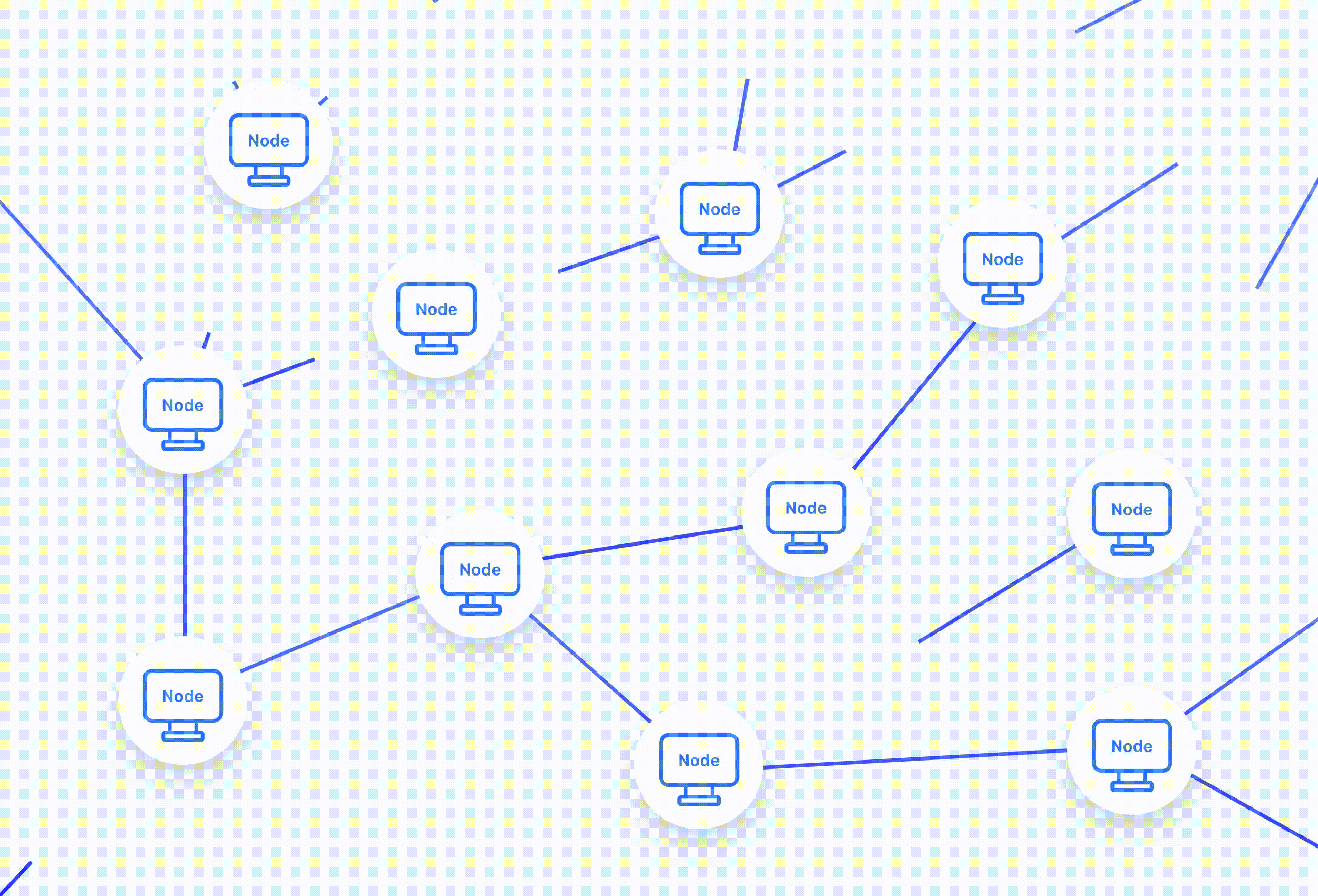
Nodes make up the blockchain network and are the only way to access it.
Each node maintains its own copy of the blockchain and works to ensure this copy checks out with all the other nodes and their respective copies. Anytime you do anything and a new block needs to be added to the blockchain, every single node on the network has to process it.
Each node chooses to accept or reject the newest block based on the validity of its signatures and transactions. If the block is accepted then it continues to be shared with other nodes until a consensus is reached and they are all in sync. Nodes are quickly able to reject invalid blocks and identify bad nodes that are attempting to break the rules. It’s this network of nodes constantly communicating that makes it possible to not need to rely on a single source of truth and all the problems that come with it.
This consensus among different nodes makes blockchain networks decentralized and is the backbone of Web3. The more nodes there are running, the stronger the blockchain becomes!
What are the different types of nodes?
There are three types of nodes:
light nodes
full nodes
archive nodes.
A light node downloads only the block headers, which is the minimum data it needs to transact on the network. A light node can validate a transaction because it is able to regenerate the specific block it needs to check by using this data.
This enables light nodes to efficiently interact with the network and save megabytes of bandwidth and gigabytes of storage. Because of this, light nodes can run on everyday devices with limited memory resources, like smartphones and laptops.
But light nodes also have their limitations. Light nodes will sometimes need to ask full nodes for the data they don’t have access to, which could take longer than a full node validating the transaction.
While a light node is the easiest way to run a node, it still takes time and know-how to install the client, configure variables, download block headers, and check to ensure that everything is running smoothly.
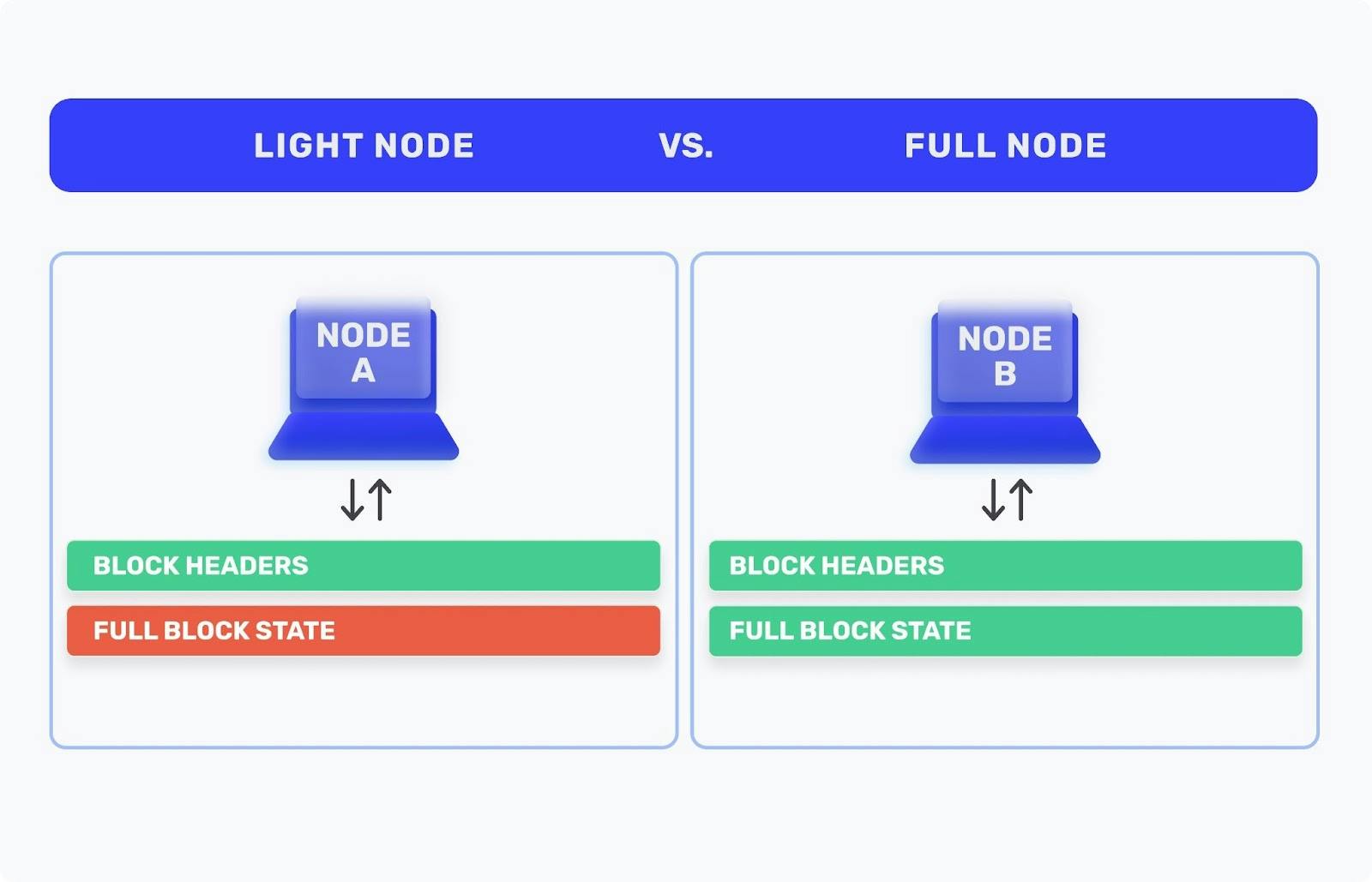
A full node has everything it needs to verify that the blocks on the network are correct. It can interact with any smart contract and deploy its own.
The full use and storage of data means that full nodes require a lot more computing and bandwidth resources. A full node downloads, stores, and verifies the full blockchain state - everything from block zero to the most recent block (+10M and counting), which can take weeks to sync!
An archive node goes one step further than a full node. While a full node trims entries that it no longer needs to verify, the latest interactions with the chain, the archive node maintains everything (terabytes of extra data). These details are great for querying information more efficiently and handy for a few applications, but are excessive in most cases.
Why is running a node difficult?
Getting a node up and running can be a lengthy and challenging process. This is especially true if you are new to the Web3 world and don’t have the technical expertise (at least, not yet).
Just the potential weeks it takes for a full node to sync to all +10M nodes for the current state of blockchain can turn off many from building in the space.
Costs are also a factor, and they can add up quickly. These include the high initial investment to purchase hardware and the ongoing costs of electricity and server hosting. When operating a node you have to also make sure it is constantly in operation. Laggy internet, electric outages, or hardware issues can lead to costly downtime.
While client updates help to constantly improve the scalability, security and sustainability of Ethereum, these changes can lead to unexpected issues. And the problems really begin when you try to build something bigger!
What are some problems with scaling Ethereum nodes?
Ethereum nodes were never really designed to scale to this level of requests and can pose some unique challenges.
Reliability
Some requests will ask the node to query all the way back from log zero to the current block and can time out. These “queries of death” can crash a node and can happen at any time of the day. Even if a node is 72% reliable like a standard node, that means that an application can be offline for over a hundred days a year!
Scalability
Scaling node infrastructure can be tricky. Imagine the application you’re building goes viral overnight on Twitter but the existing nodes you’re running can’t keep up with the sudden spike in traffic and transaction volume.
You can’t just quickly spin up new nodes because they take weeks to sync. On top of that, the new demand could overwhelm your existing nodes and cause them to crash. This could result in downtime, where no one can use your application, and unhappy users who don’t think they can rely on what you’ve built!
Data Consistency
In Web2, sites are able to work around these issues of scalability by using load balancers, a network layer that sits on the top and distributes traffic across indistinguishable servers. This isn’t possible with nodes because blockchain is asynchronous. While two nodes should share an identical latest block eventually, at any given time, one might lag behind another.
Load balancing could lead to two very different results because traffic is routed through different nodes with different views on the latest block. Imagine buying that NFT you’ve been coveting but then refreshing to find that it seems to have disappeared!
Attempting to avoid these sort of data inconsistencies leads developer teams to patch together complex workarounds that inevitably cause errors and crash their application. All these problems mean that when dealing with nodes, developers often must choose between scaling, maintaining reliability or ensuring consistent data, which leads to a less than ideal experience for everyone.
When to use node-as-a-service?
If this all seems a bit overwhelming, don’t worry! Whether you’re just getting started or think you’re spending too much time and money on node problems, then nodes-as-a-service might be the solution for you.
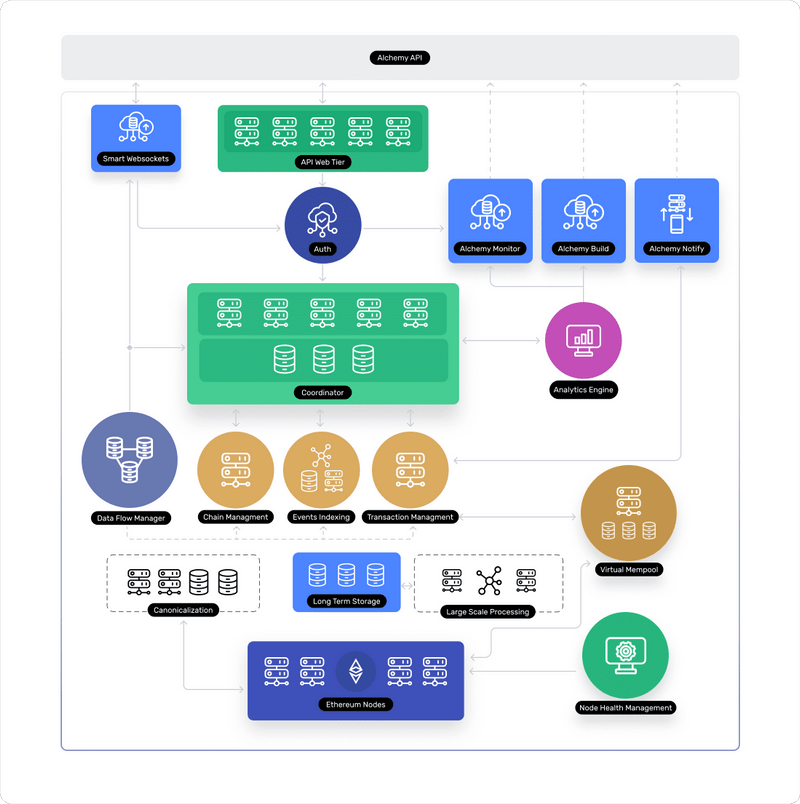
Node providers like Alchemy run nodes so you can focus on developing your application. It’s incredibly easy to integrate most providers - it’s often just an API to get started reading and writing onto the blockchain.
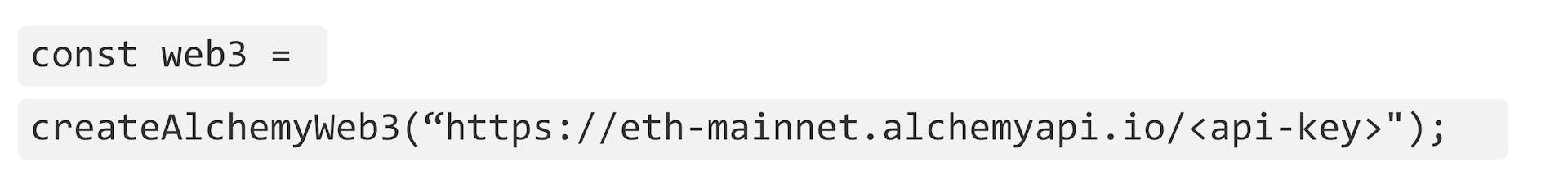
That means instead of having to pay for server access, meet hardware requirements and maintain state all by yourself, you can use Alchemy's Supernode infrastructure…
… with a single line of code.
Alchemy is able to ensure supercharged data correctness through a proprietary coordinator service and best-in-class reliability. They do this through a dedicated, distributed system allowing you to scale quickly and seamlessly to help you build better and ship faster.
"Using your own node or an error-prone service means wasting hundreds of valuable engineering hours on problems that have nothing to do with your company. Nothing else compares to Alchemy's amazing level of reliability, speed, support." - Alex Atallah, CTO OpenSea
Leading blockchain companies and projects like OpenSea, Dapper Labs, 0x, Royal, Axie Infinity, and hundreds more all choose Alchemy because of our incredibly high reliability, legendary customer service, and amazing suite of products that makes building in Web3 more accessible than ever.

Sign up for an Alchemy account and get started building right away without having to worry about nodes! If you’re interested in learning more about how Alchemy can help you in your journey to build in Web3, check out our Getting Started With Alchemy documentation and reach out to us 24/7 on our Alchemy Discord.

Related overviews
Looking for the best Hyperliquid RPC in 2026? This guide showcases the best providers.
Learn about the role of indexers and how they help you query onchain data.
Understand the differences between permissioned and permissionless chains and how to choose the right one.

Build blockchain magic
Alchemy combines the most powerful web3 developer products and tools with resources, community and legendary support.