
What is an Ethereum Node-as-a-Service?
Written by Alchemy
RPC nodes are an essential piece of blockchain infrastructure because they allow anyone in the world to send and request information and transactions to the blockchain. Because running your own node is an expensive financial investment, in terms of hardware and maintenance costs, web3 startups look for more cost-effective solutions including Ethereum Node-as-a-Service companies, or companies that maintain nodes for developers to access for a monthly or annual fee.
This article will explore what Ethereum NaaS providers do, and how to decide if using a NaaS provider is the best node infrastructure choice.
What is an Ethereum node?
An Ethereum node connects a computer to the Ethereum blockchain by running software (“the client”) which can exist either on the consensus layer (for validation) or the execution layer (for processing transactions). Every batch of proposed (i.e. pooled or pending) transactions is propagated to each node in the network, and these nodes either accept or reject the new block through a validation process.
A node is the only way to access information from the blockchain, as there is no central portal to access data from. A larger number of nodes also makes a blockchain more robust and secure, decreasing the ease of launching a 51% attack.
There are three different types of nodes:
1. Full Nodes
Full nodes contain all the information in a given blockchain, with some exceptions for periodic pruning. Full nodes can verify any transaction, and can interact with and deploy smart contracts. Setting up a full node can take weeks to configure and sync due to the amount of data they store.
2. Archive Nodes
An archive node stores the entire, unpruned transaction history on a blockchain. While archive nodes can use terabytes of data, they can be especially useful for developers looking to debug and inspect transaction history at a granular level. Archive nodes are essential for services like block explorers, wallets, and blockchain analytics companies.
3. Light Nodes
Light nodes contain only the block header information, representing only a summary of the data. Light nodes can access the blockchain, however, they do not serve as part of consensus verification. Light nodes can run on mobile devices and are more accessible to the larger public because of their lower hardware and software requirements.
What does Ethereum Node-as-a-Service (NaaS) mean?
Ethereum Node-as-a-Service (NaaS) providers serve as an alternative to managing Ethereum nodes in-house, where users can send requests through a service providers APIs using a dedicated API endpoint. Another name for companies that offer Ethereum NaaS service is "node provider."
Web3 NaaS providers are analogous to platforms like Amazon Web Services (AWS), which allow web2 applications like Netflix, Expedia, and Linkedin to run their cloud applications on another company's infrastructure.
Node providers can guarantee more reliable infrastructure to build on, complimentary developer tools, analytics, and advanced APIs designed for specific web3 use cases such as NFT API endpoint, transaction API endpoints, and debugging API endpoints.
Types of Ethereum Node-as-a-Service Providers
There are two types of Ethereum NaaS providers: platforms which provide individual nodes to customers, and platforms which provide scalable access and throughput to a network of nodes.
The main difference between providers that give access on a per-node basis, versus companies like Alchemy that provide Ethereum Node services on an on-demand basis is scalability. If you pay for a single node, you are limited by a single node's scale, whereas if you subscribe to Alchemy, you can scale infinitely, on-demand, through and entire fleet of nodes.
There are a variety of companies that serve as node providers including Alchemy which offer the most reliable and affordable nodes on the market. Ethereum NaaS providers like Alchemy are used both my emerging startups and large enterprises like Opensea and x2y2 for data accuracy, scale, and reliability.
What are the benefits of using an Ethereum NaaS provider vs. running your own full node?
The benefits of using a Ethereum NaaS solution instead of running your own node is reliable uptime, no overhead costs, infinite scalability, 1-line integration, a variety of APIs and tools, and technical support.
For example, Alchemy’s Supernode boasts 99.99% reliability, dynamic scalability, the best data correctness, testnet support, and a variety of enhanced APIs like Webhooks, all within the same platform.
Because NaaS systems are easy to integrate, it only takes a few lines of code and an API key to get started, unlike running a node in-house, which could take weeks to configure and synchronize with Ethereum's state.
What are the tradeoffs of using an Ethereum NaaS provider vs. managing your own nodes?
Even though using an Ethereum NaaS provider comes with a host of benefits, there are two common trade-offs compared to running your own node: centralization and customization.
Because dApps can change to an alternate RPC endpoint at any time, the tradeoff of Ethereum NaaS providers being a "centralizing" force is not a critical concern. The centralizing factor is instead of managing your own node, you are trusting a centralized provider to ensure their node infrastructure is live.
Additionally, using your own node allows for maximum node client software customization, allowing you to run your own RPC endpoints (for personal or public use), with your choice of execution and consensus layer software.
How to Use an Ethereum Node Provider
Working with a node provider is fairly simple. To start using Alchemy's Ethereum nodes, simply sign up, create an app, and copy/paste your RPC endpoint URL into your application.
1. Sign Up for a Free Alchemy Account
Making an Alchemy account is quick and easy, visit alchemy.com and get started for free. Once you sign in, you'll be placed on the Alchemy dashboard, where you can create a new Ethereum app.
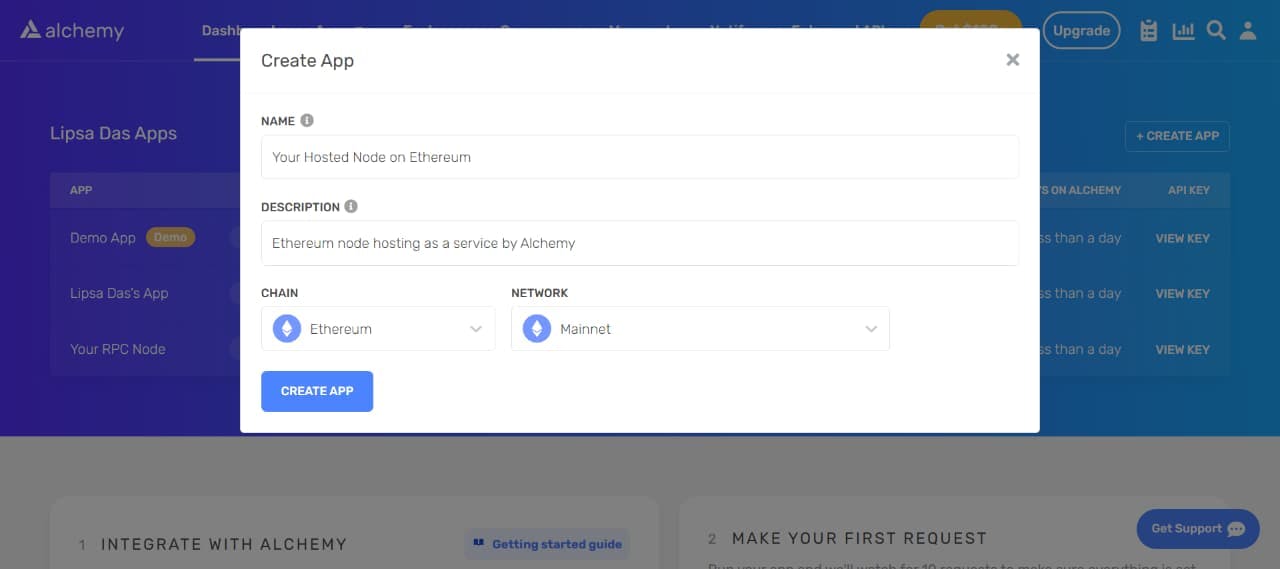
2. Create a New Ethereum App
To create a new app, you should:
Navigate to the Apps section from your Dashboard
Click the “Create App" button
Name your app and include a description
Choose "Ethereum" as the chain
Choose either "Mainnet" or "Goerli" (an Ethereum testnet)
Click "Create App"
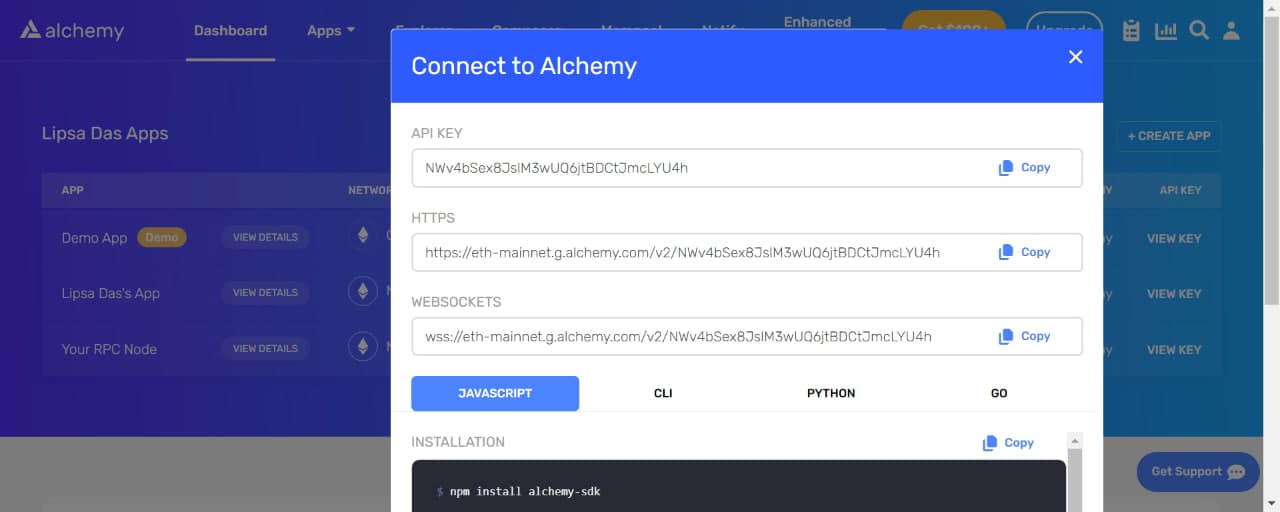
3. Paste Your API Key Into Your App
In your list of Apps, click the "View Key" button to see your API keys. Next, click "Copy" next to the HTTPS link. Now, replace your current Ethereum RPC endpoint in your application with this new link to start sending Ethereum transactions and requests through Alchemy.
With an Ethereum node endpoint, you can use all of Alchemy’s integrated developer tools!
Start Building on Alchemy's Ethereum Node Infrastructure
Building and maintaining your own nodes is time-consuming, expensive, and difficult. Ship your minimum viable product, acquire real users, and find product-market fit faster by building on Alchemy's infinitely scalable and highly reliable node infrastructure.

Related overviews
Looking for the best Hyperliquid RPC in 2026? This guide showcases the best providers.
Learn about the role of indexers and how they help you query onchain data.
Understand the differences between permissioned and permissionless chains and how to choose the right one.

Build blockchain magic
Alchemy combines the most powerful web3 developer products and tools with resources, community and legendary support.