
Kintsugi vs. Kiln testnet
Written by Alchemy
Note: As of September 12th, 2022, the Kiln testnet was deprecated by The Ethereum Foundation, and Alchemy's Kiln faucet was deprecated on September 26th, 2022.
As the Ethereum blockchain matures, more test networks have emerged to help core developers and Ethereum dApp developers prepare for Ethereum’s upcoming merge to proof of stake. Two of the testnets, Kintsugi and Kiln, focus on preparing for the upcoming launch of Ethereum’s new consensus layer upgrade.
This article will compare the Kiln and Kintsugi testnets and show how to use them.
What are the similarities between the Kiln testnet and the Kintsugi testnet?
The biggest similarity between Kiln and Kintsugi is their consensus mechanism: proof-of-stake (PoS) instead of proof-of-work (PoW). Having undergone the long-anticipated Merge, both Kiln and Kintsugi use the eco-friendly consensus layer with cheaper gas. The client developer intends this transition from PoW to PoS to uncover any major issues before the completion of the Merge later this year.
The Kintsugi test blockchain was launched by the Ethereum Foundation as an Ethereum community initiative in December 2021. Kintsugi was the first “longer-lived public testnet” intended for initial merge testing. Similarly, the Kiln testnet was launched by Ethereum in March 2022 as the second testnet to experiment with the post-merge environment.
Both merge testnets are shadow forks of the Ethereum chain. Thus, they are identical to the Ethereum chains and thus are completely EVM-compatible.
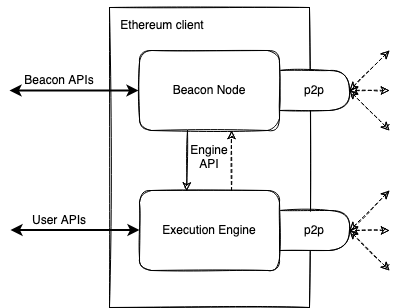
As the testnets simulate post-merge environments, they use Beacon nodes and Execution engines in their consensus clients, handled by the existing execution layer client (pre-merge).
While both layers maintain independent API endpoints, they are intertwined with peer-to-peer connections to bridge the Eth1 clients with the PoS mechanism of Beacon chains.
More information about Ethereum’s post-merge architecture can be found in Tim Beiko’s AllCoreDevs update 007 on Mirror.
What are the differences between the Kiln testnet and the Kintsugi testnets?
The main difference between the Kiln and Kintsugi testnets is one is still active and the other is deprecated. In its early months, the Kintsugi testnet experienced major client bugs that resulted in the network forking twice. Soon after, the Kiln testing network was launched with improvements to re-test the post-merge environment. After the launch of the Kiln testnet, the Kintsugi network was officially deprecated.
Should I use the Kiln testnet or the Kintsugi testnet?
Since the Kintsugi and Kiln testnet are officially deprecated, we recommend developers use the Sepolia testnet to test their dApps, as Alchemy has full Sepolia support and a free Sepolia faucet.

Related overviews
Building on Base? Get free Sepolia ETH and start testing your app!
Learn How to Migrate to the New Ethereum Testnet Sepolia From Goerli
Migrating dApps and Bridging Goerli ETH to Optimism

Build blockchain magic
Alchemy combines the most powerful web3 developer products and tools with resources, community and legendary support.